1. INTRODUCTION
I completed the Vulnerability Assessment module on HackTheBox.
2. SECURITY ASSESSMENTS
The module started by explaining what a vulnerability assessment is and how it differs from a pentest. Essentially, a vulnerability assessment seeks to discover low-hanging vulnerabilities while a pentest is a simulation of how those vulnerabilities can be used by attackers to attack the system. The section also explained the types of pentests: blackbox, graybox, and white box which differ depending on the amount of information or access that the tester is given to work with, black being the least. We also analyzed other types of security assessments: bug bounties, blue-, red-, and purple teams.
3. VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENTS
This was now a deeper dive into vulnerability assessments: what they are, the methodology, and various terms that are used with regards to this type of security assessment. It also explained the terms used: threat, vulnerability, and risk. A new incident with potential to harm the system, plus a known weakness result in a risk: potential for damage.
4. ASSESSMENT STANDARDS
Then we moved to standards. PCI, HIPAA, FISMA, and the famous ISO 27001 which I had seen a couple of times and never really understood. The essence of this section was pretty much that penetration tests should not be performed without any rules or guidelines. There must always be a specifically defined scope for a pentest, and the owner of a network must have a signed legal contract with pentesters outlining what they’re allowed to do and what they’re not allowed to do.
5. COMMON VULNERABILITY SCORING SYSTEM (CVSS)
There are various ways to score or calculate severity ratings of vulnerabilities. This section explored two widely recognized frameworks: the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) and the Microsoft DREAD model. CVSS provides a standardized, structured method focused on exploitability and impact, while DREAD offers a more qualitative approach based on factors like damage potential and discoverability.
6. COMMON VULNERABILITIES AND EXPOSURES
OVAL is an international standard supported by DHS and NIST, designed to help automate vulnerability detection and compliance checking. It provides a structured language (in XML) for defining system states such as Vulnerable, Patched, or Non-compliant. It includes four main definition types: Vulnerability, Compliance, Inventory, and Patch. Tools like Nessus use OVAL definitions to standardize scans.
CVE is a public catalog of known vulnerabilities, each with a unique ID to standardize how issues are tracked and discussed. The module outlines how vulnerabilities are evaluated, reported, and assigned CVE IDs through a process involving the researcher, vendors, and the CVE team. Responsible disclosure is emphasized to prevent exploitation by bad actors before patches are released.
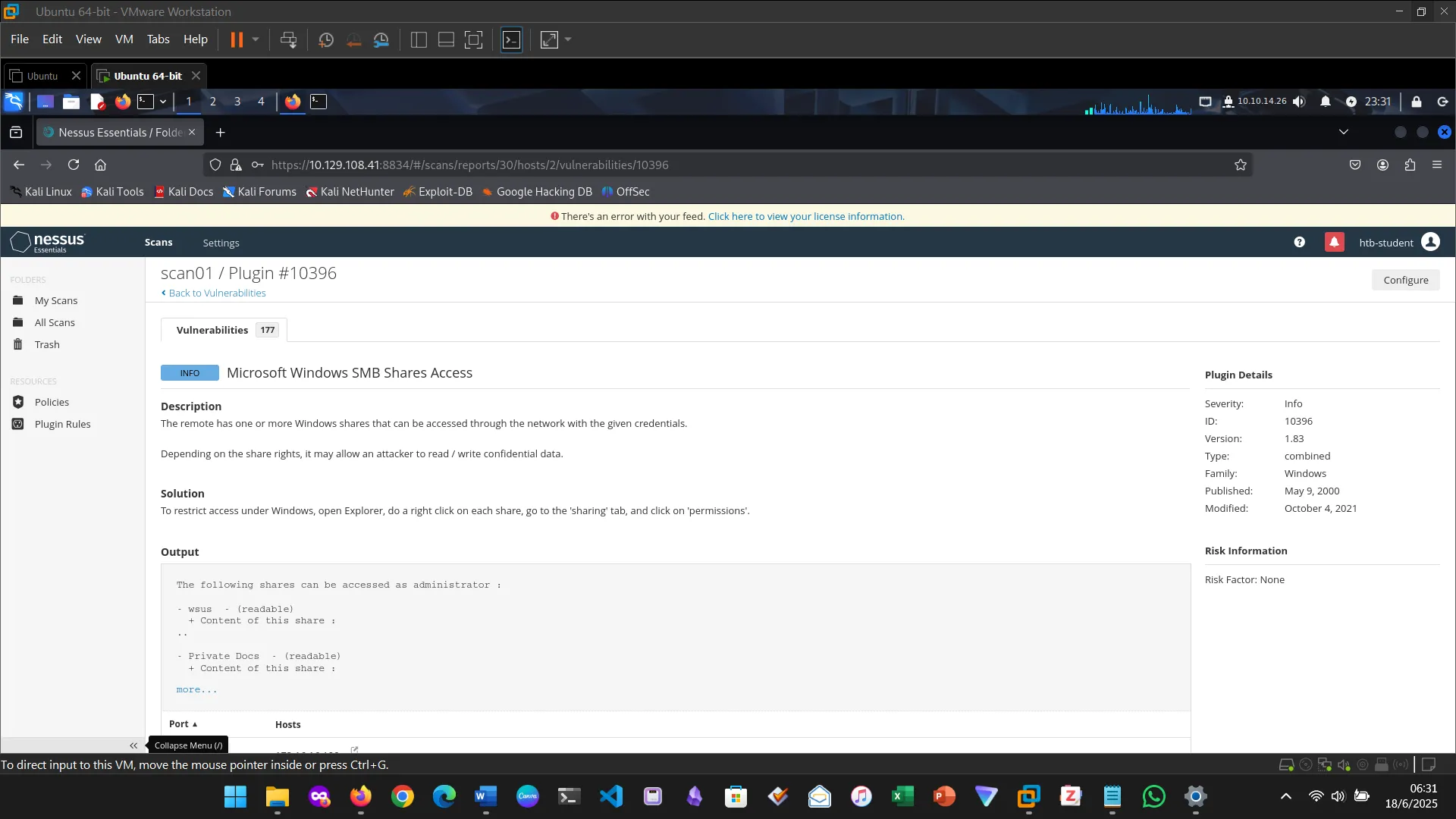
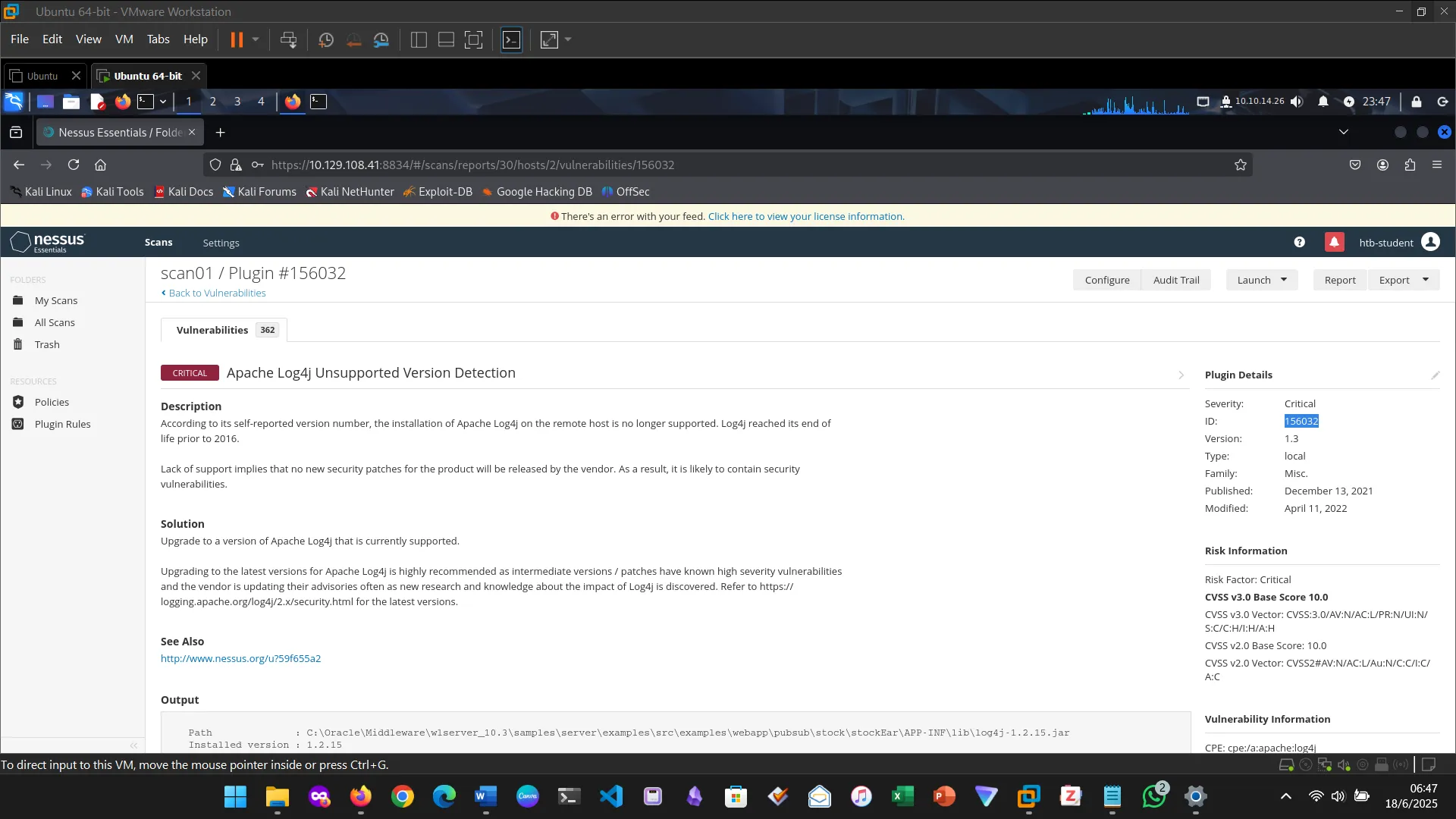
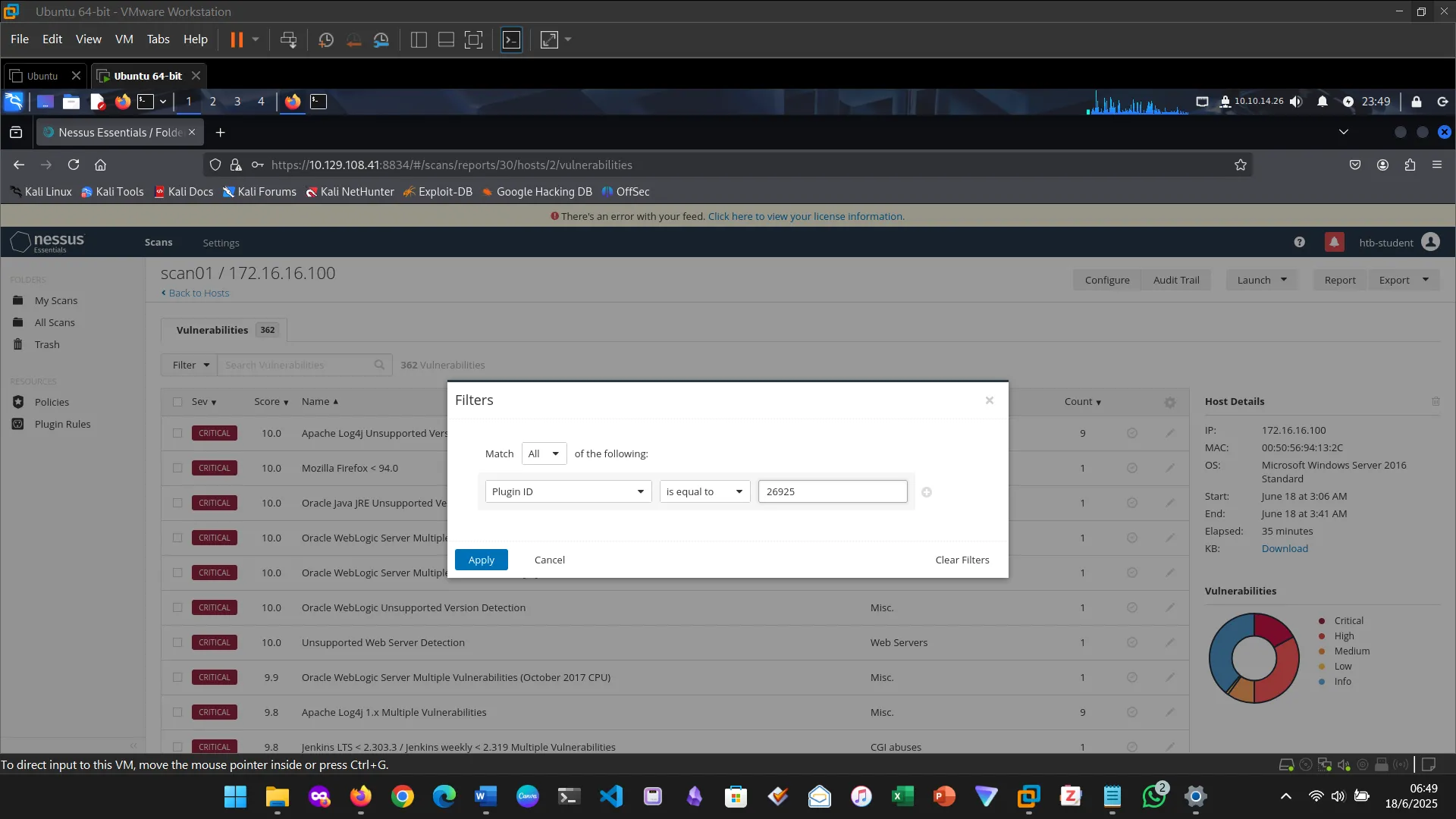
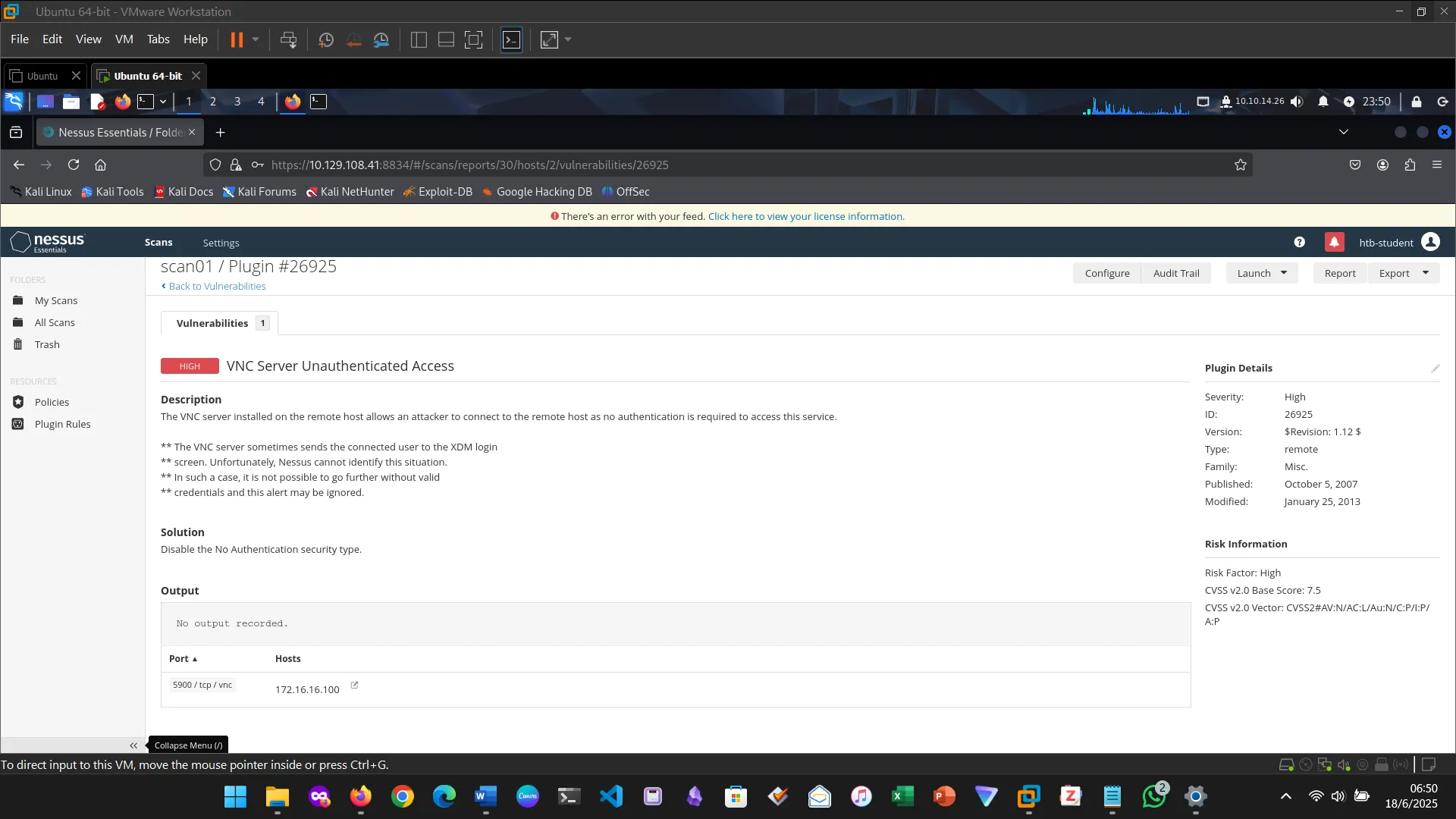
7. NESSUS
This section introduced and explored Nessus, the vulnerability scanner. First I downloaded Nessus, installed and activated it.
8. OPENVAS
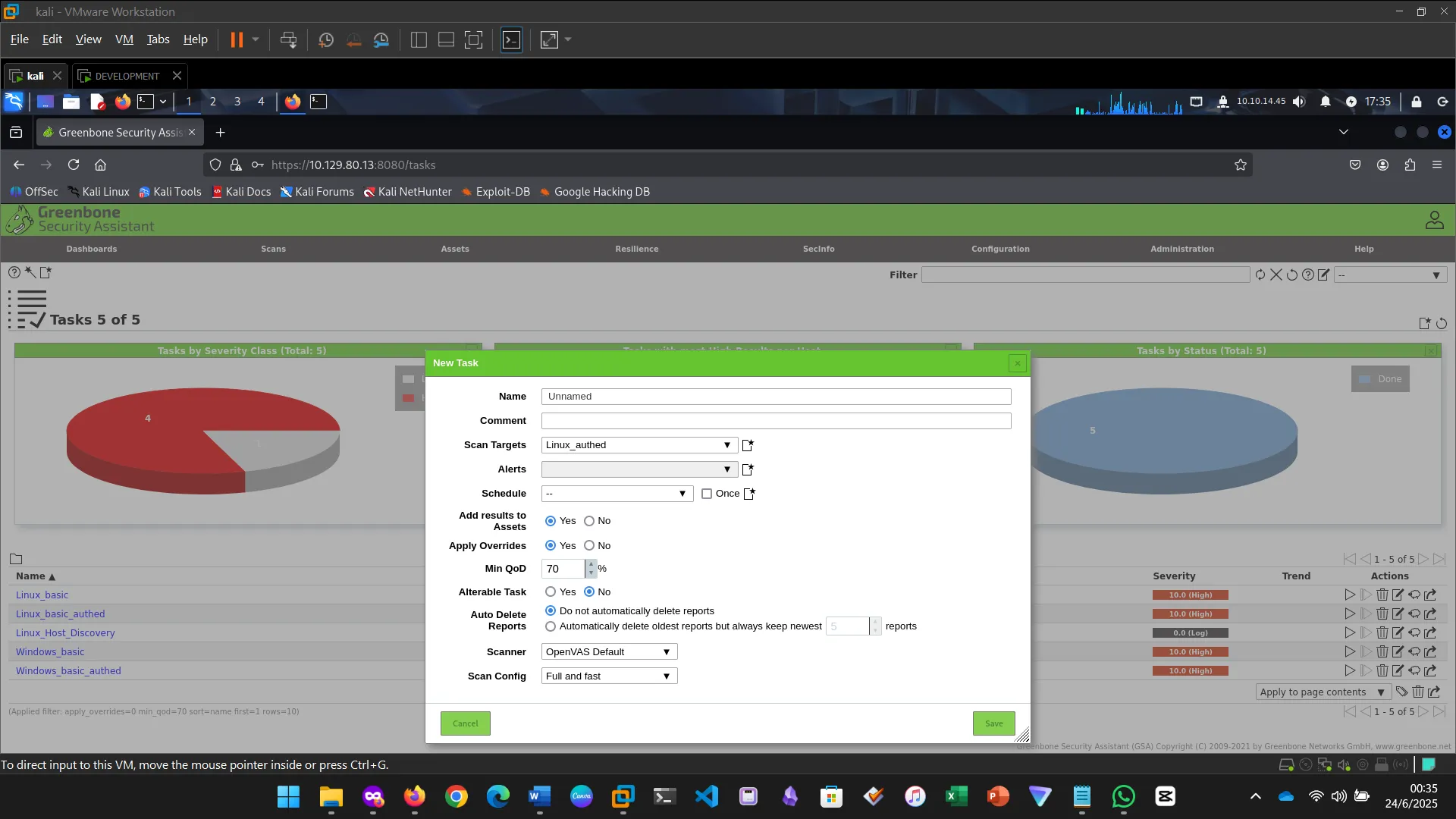
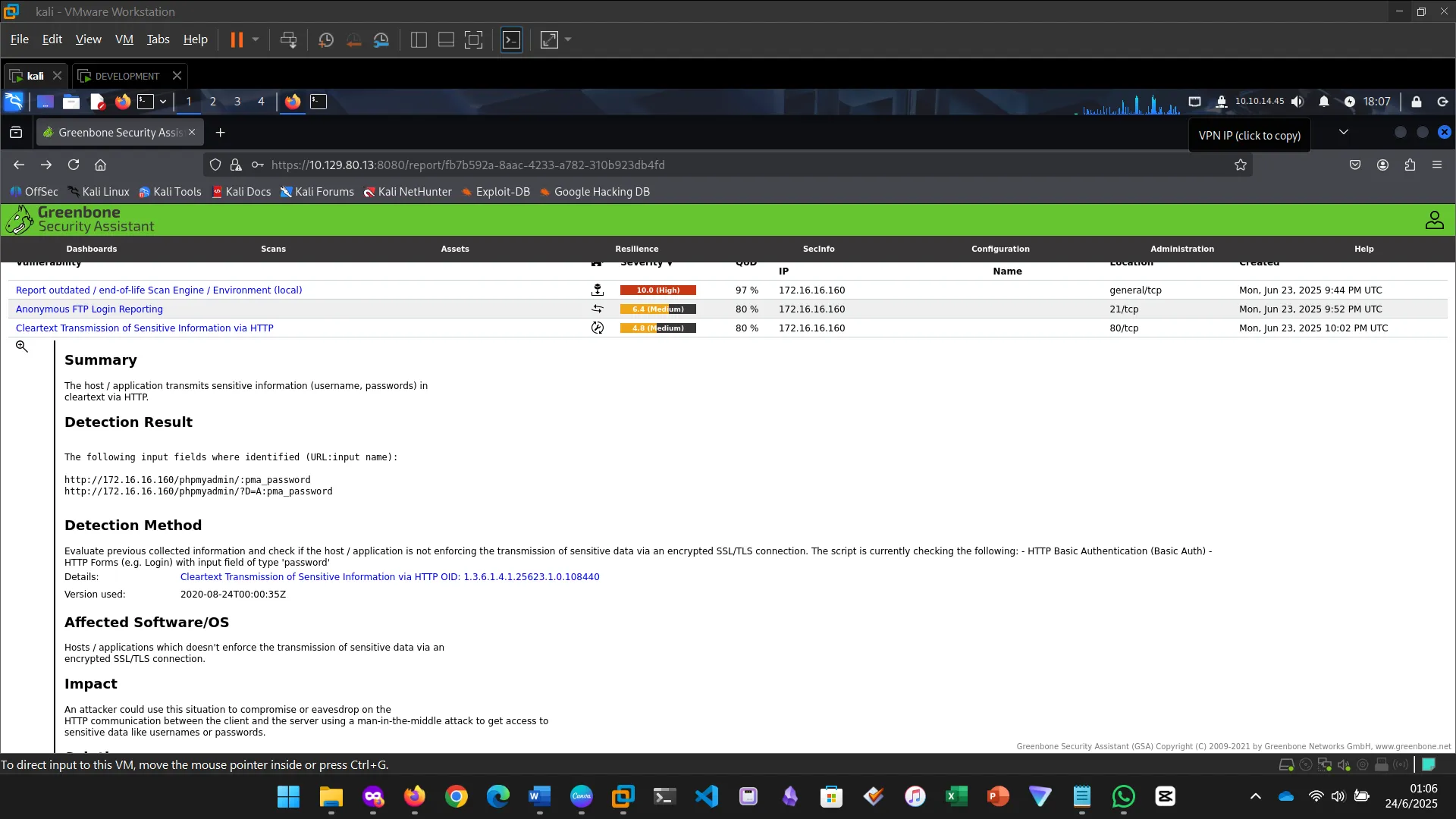
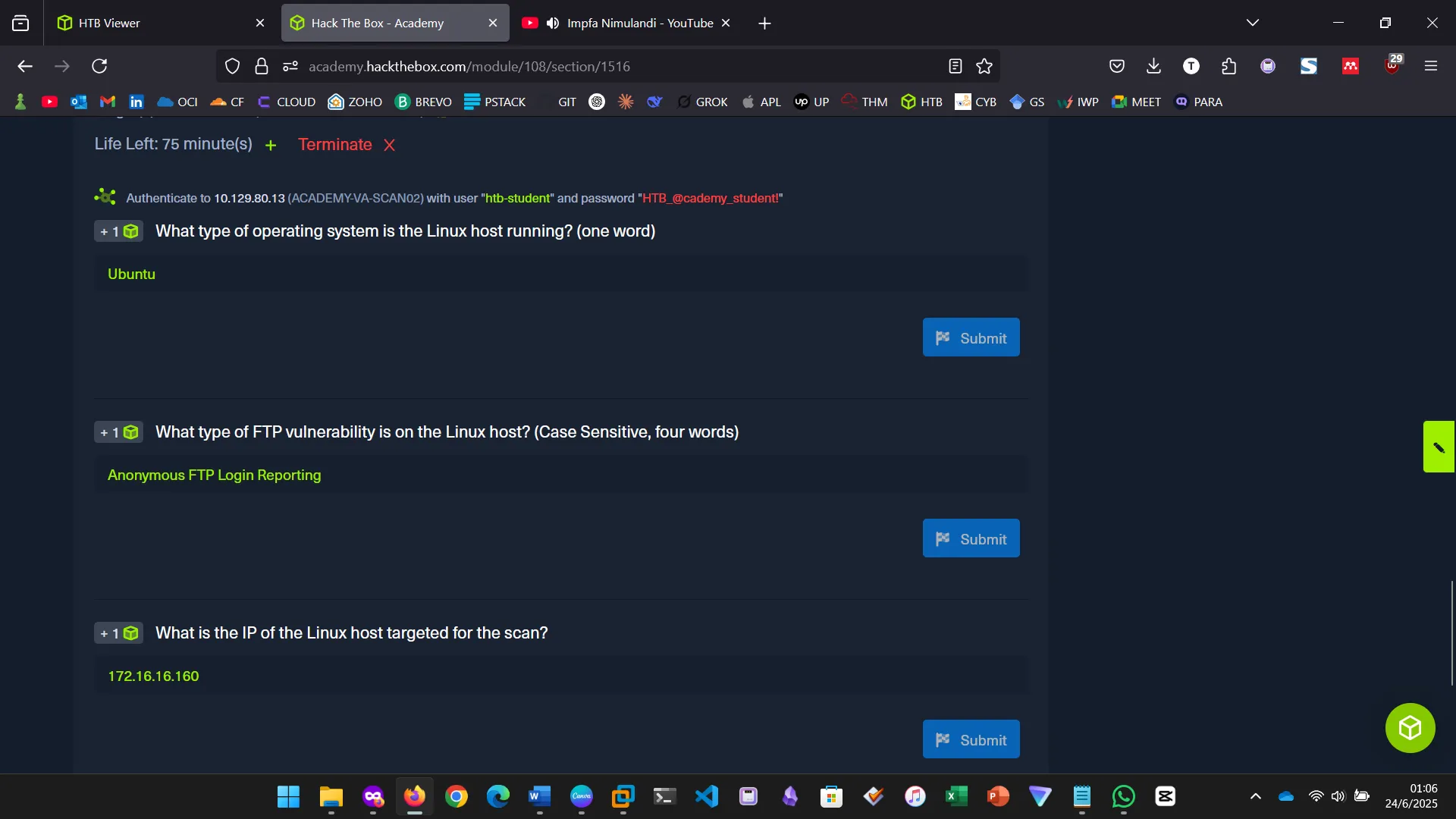
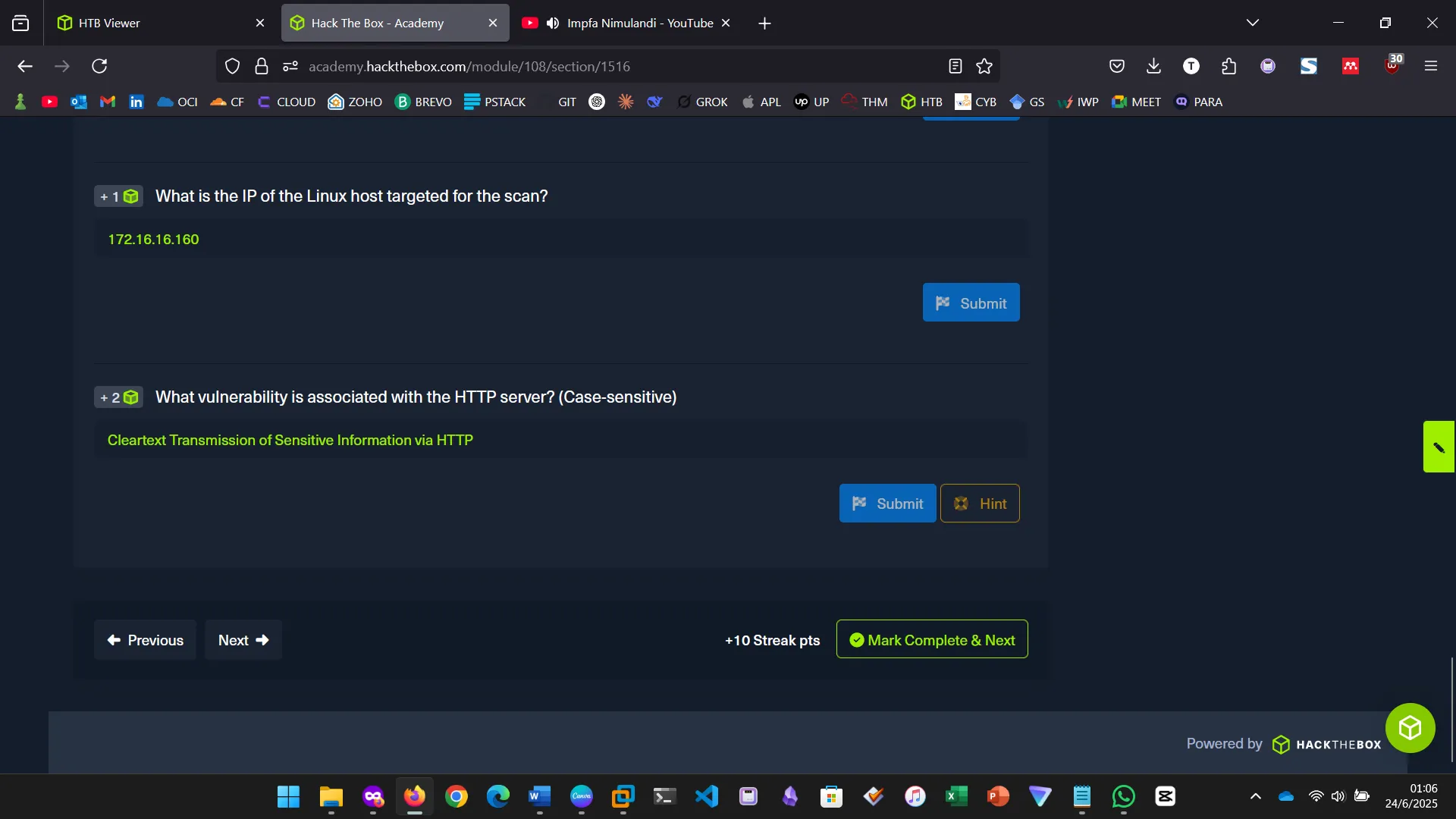
OpenVAS, by Greenbone Networks, is a publicly available vulnerability scanner that has the capabilities to perform network scans, including authenticated and unauthenticated testing. We started by installing the tool and then proceeded to perform a scan.
9. CONCLUSION
I have to say this module taught me about problem solving more than the content itself. Of course, I learned about Nessus and OpenVAS, completely new tools, but I had a hurdle with setting up the tools. Being that I prefer working on my own system, it took me some time before I could successfully install OpenVAS on my own system before I could work with the provided tools. Submitted the assignment way late but drove the lesson home. Intense.