Module: Linux Fundamentals
Student: Tapiwanashe Mlambo
1. INTRODUCTION
This module was an introduction to Linux and tackled such fundamental topics as remote access, using the BASH terminal, the filesystem and navigating the directories, services and process management, etc. It was largely revision for me, though refreshing these concepts was essential—especially now that I’m aligning them with cybersecurity.
2. THE SHELL
This section introduced the command line. I connected to a remote Linux server using SSH and found it running Ubuntu.
3. SYSTEM INFORMATION
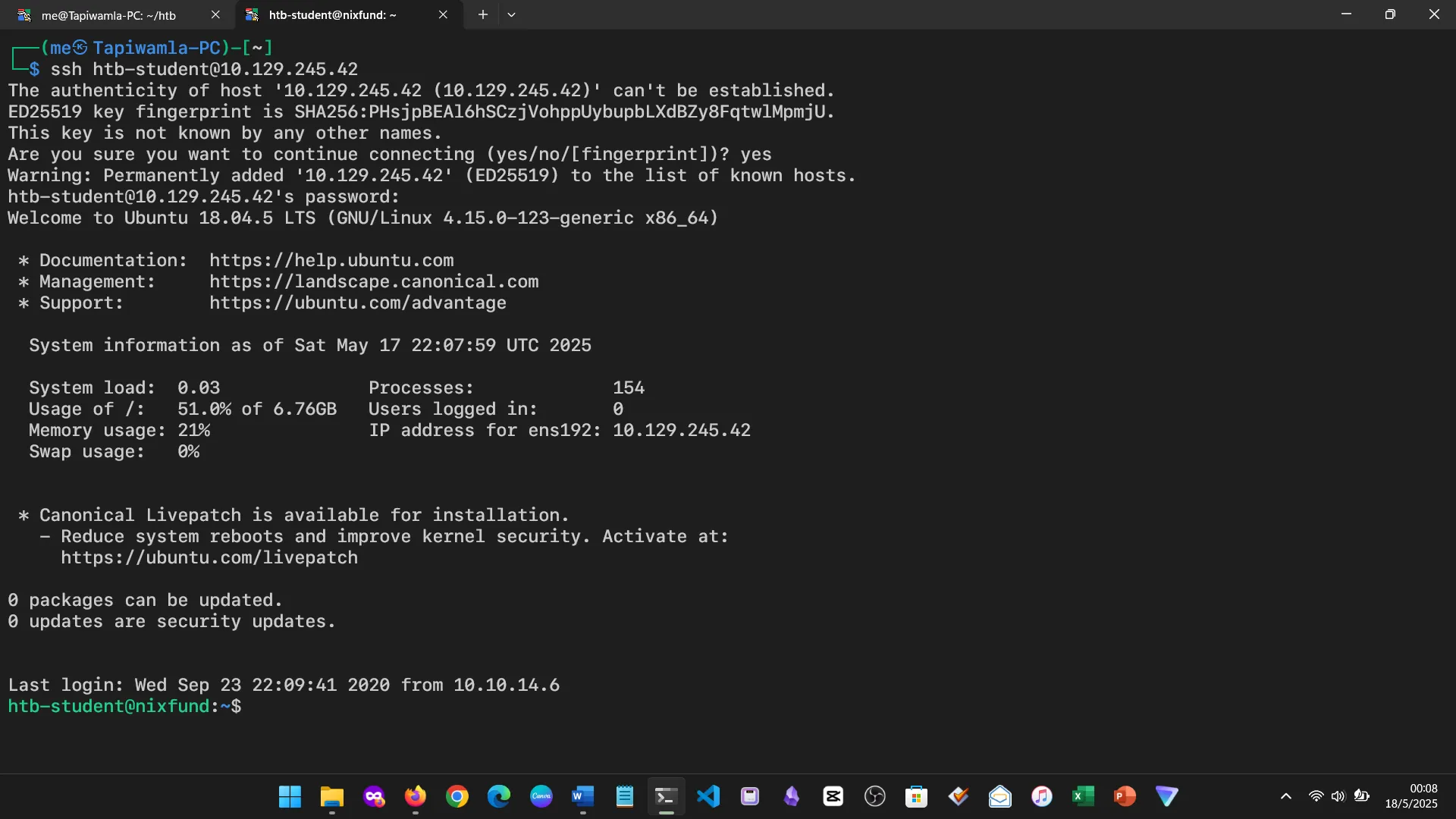
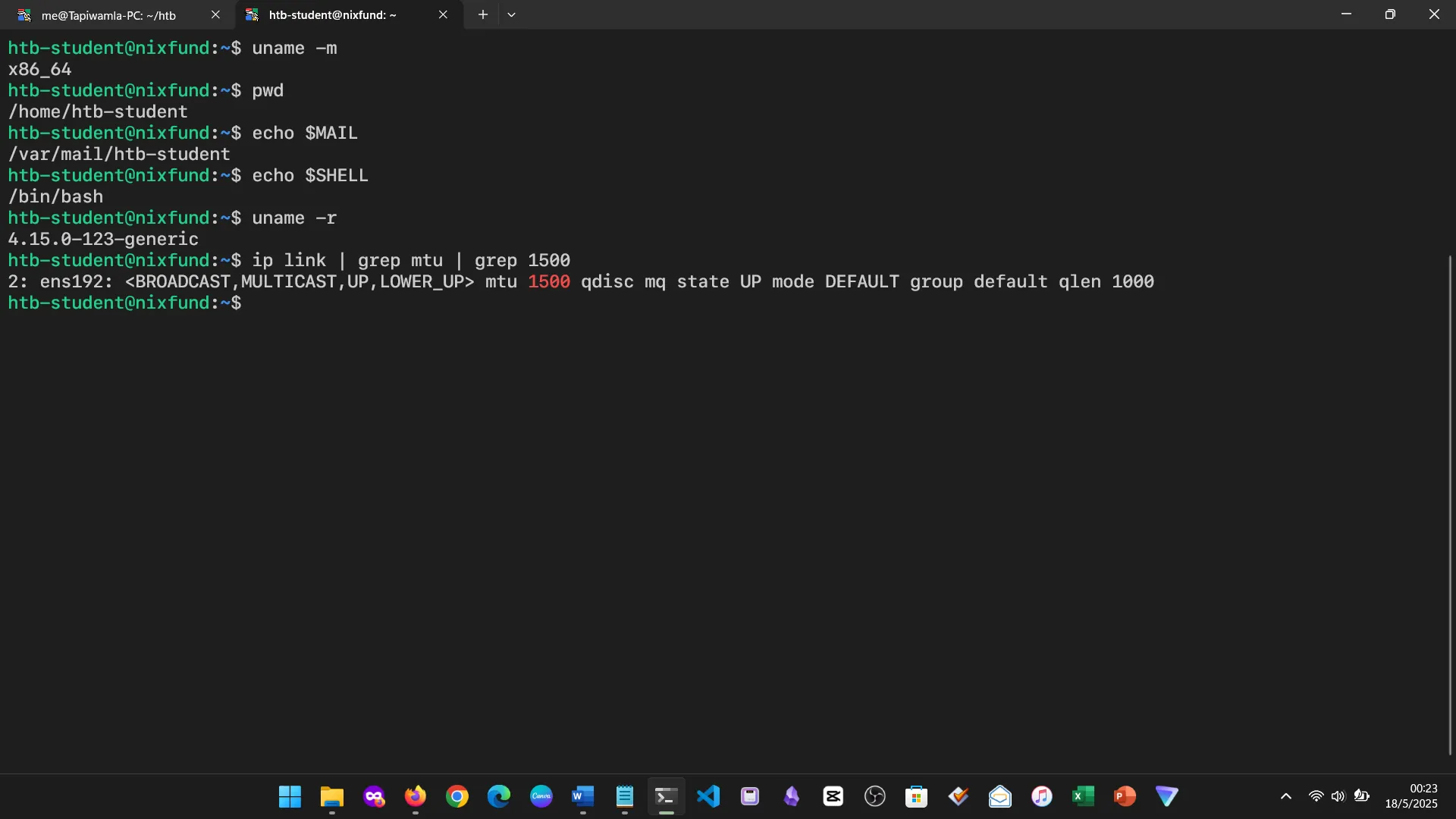
This covered system details, user identification, and secure remote login via SSH. I practiced gathering system data, checking user privileges, and confirming remote access.
4. NAVIGATION
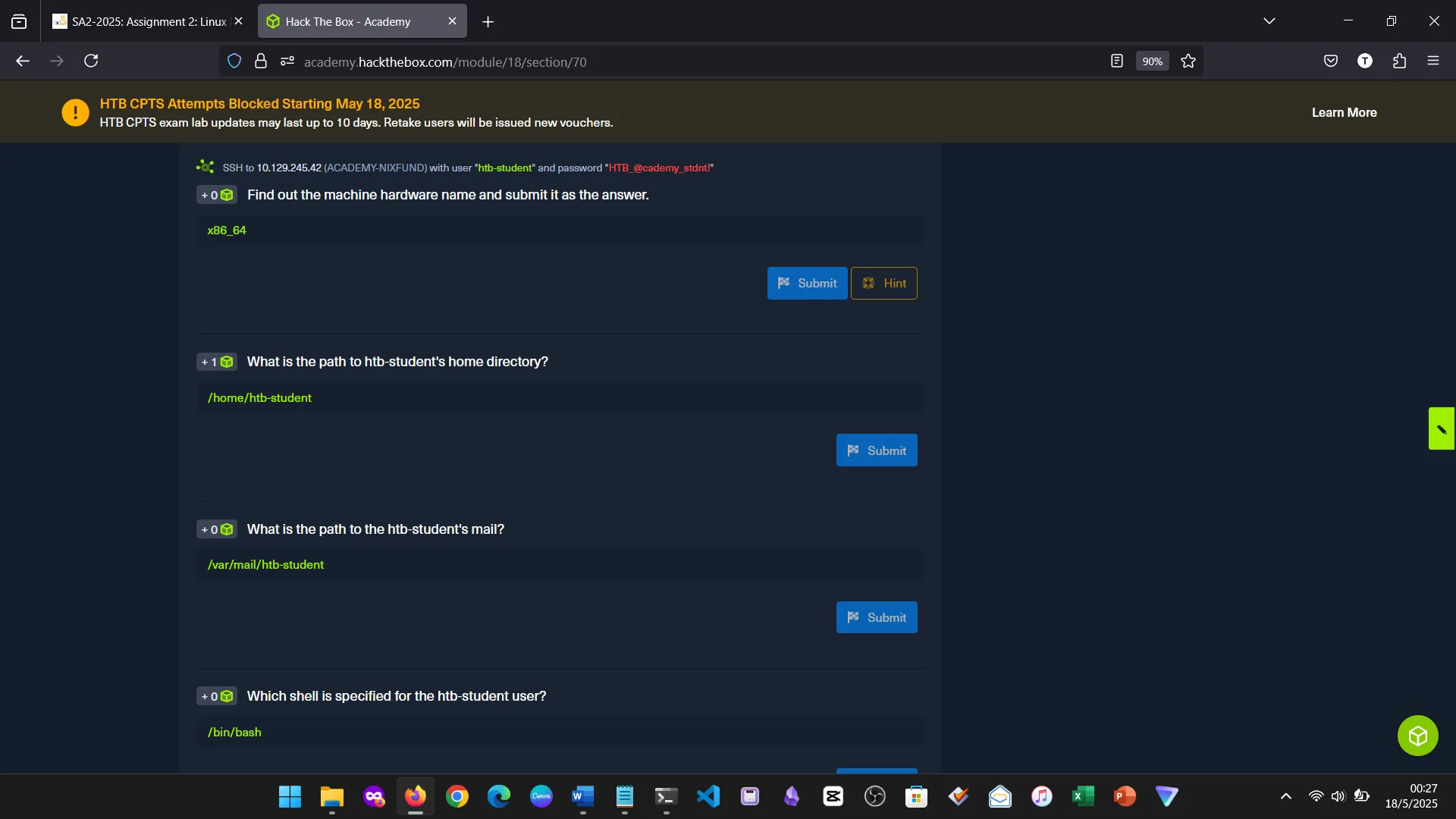
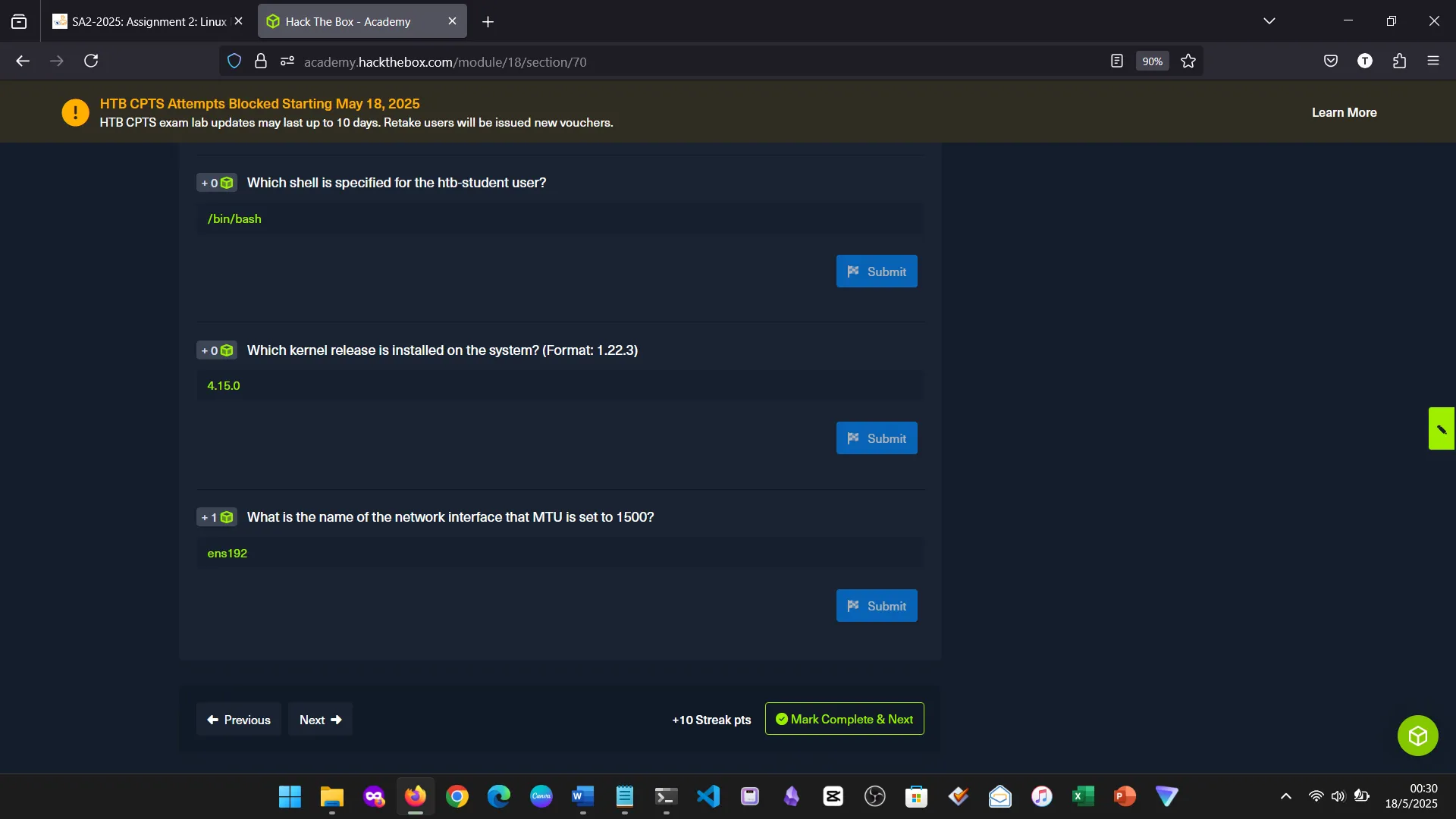
We explored Linux directory navigation, commands like pwd, ls, cd, hidden files, and shortcut keys. Linux’s precision in navigation makes it a powerful system to work with.
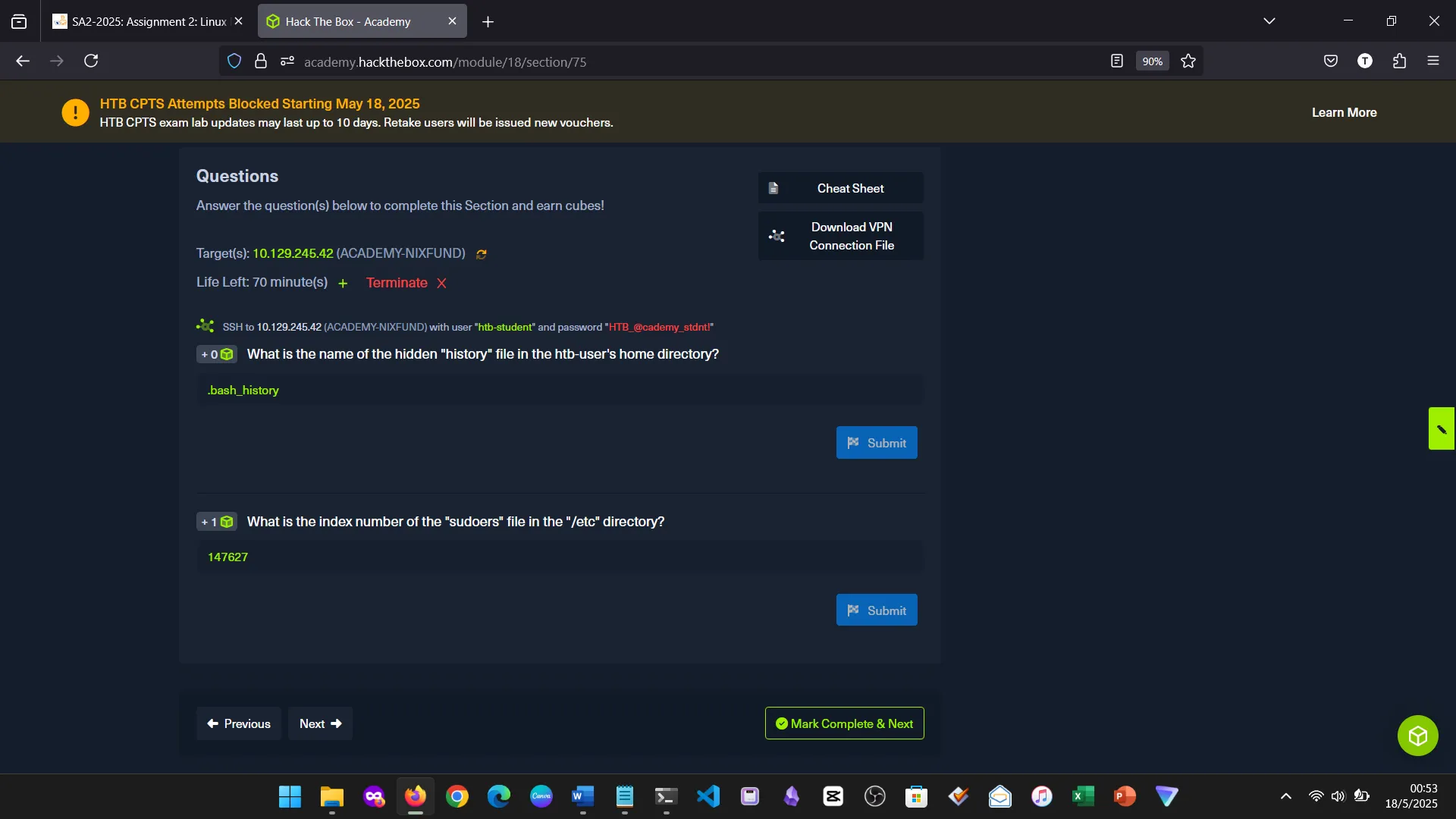
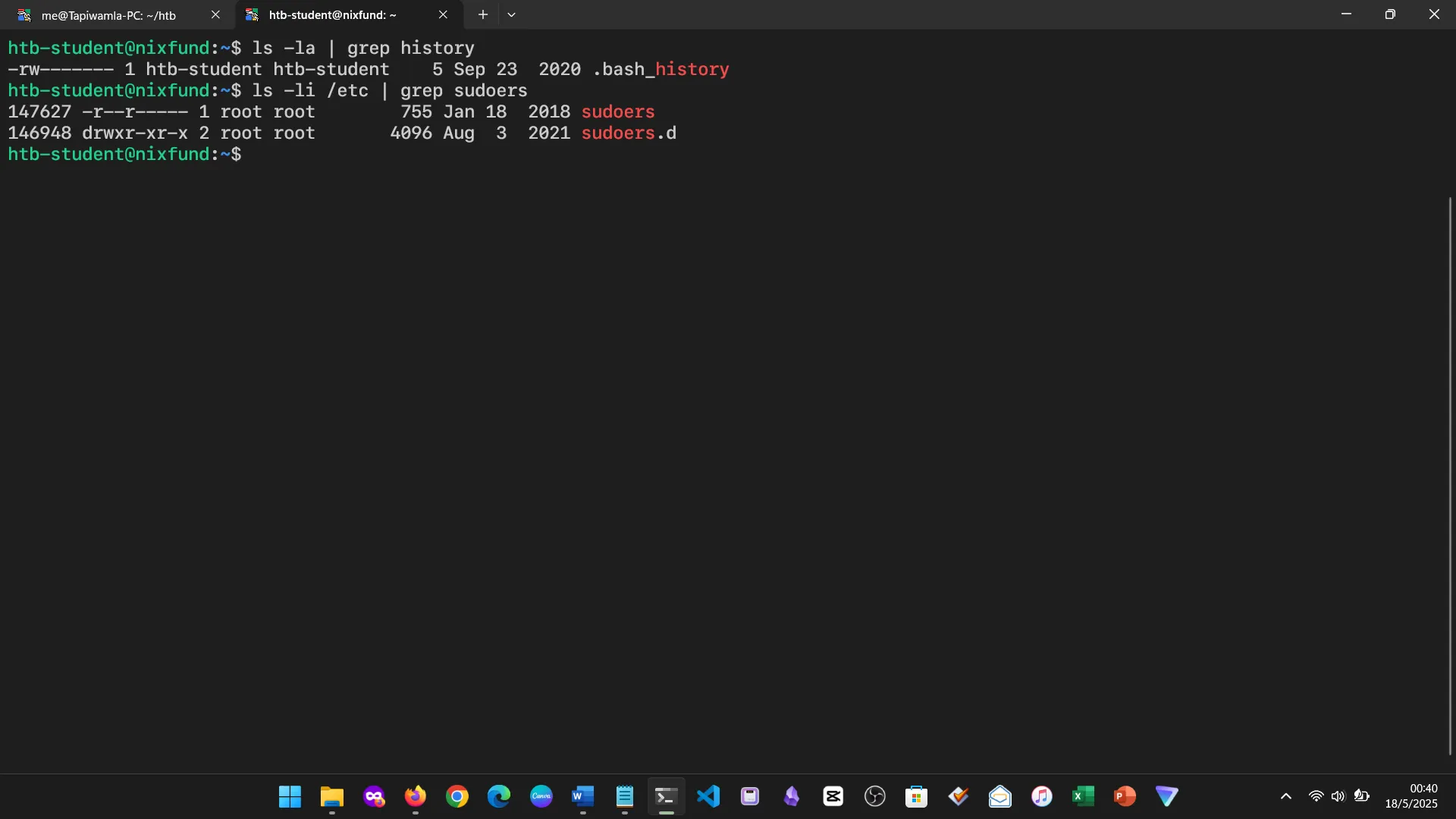
5. FILES AND DIRECTORIES
We covered directory structure, file operations, redirection, and regex-based modifications. Though familiar, I gained a new appreciation for advanced file control.
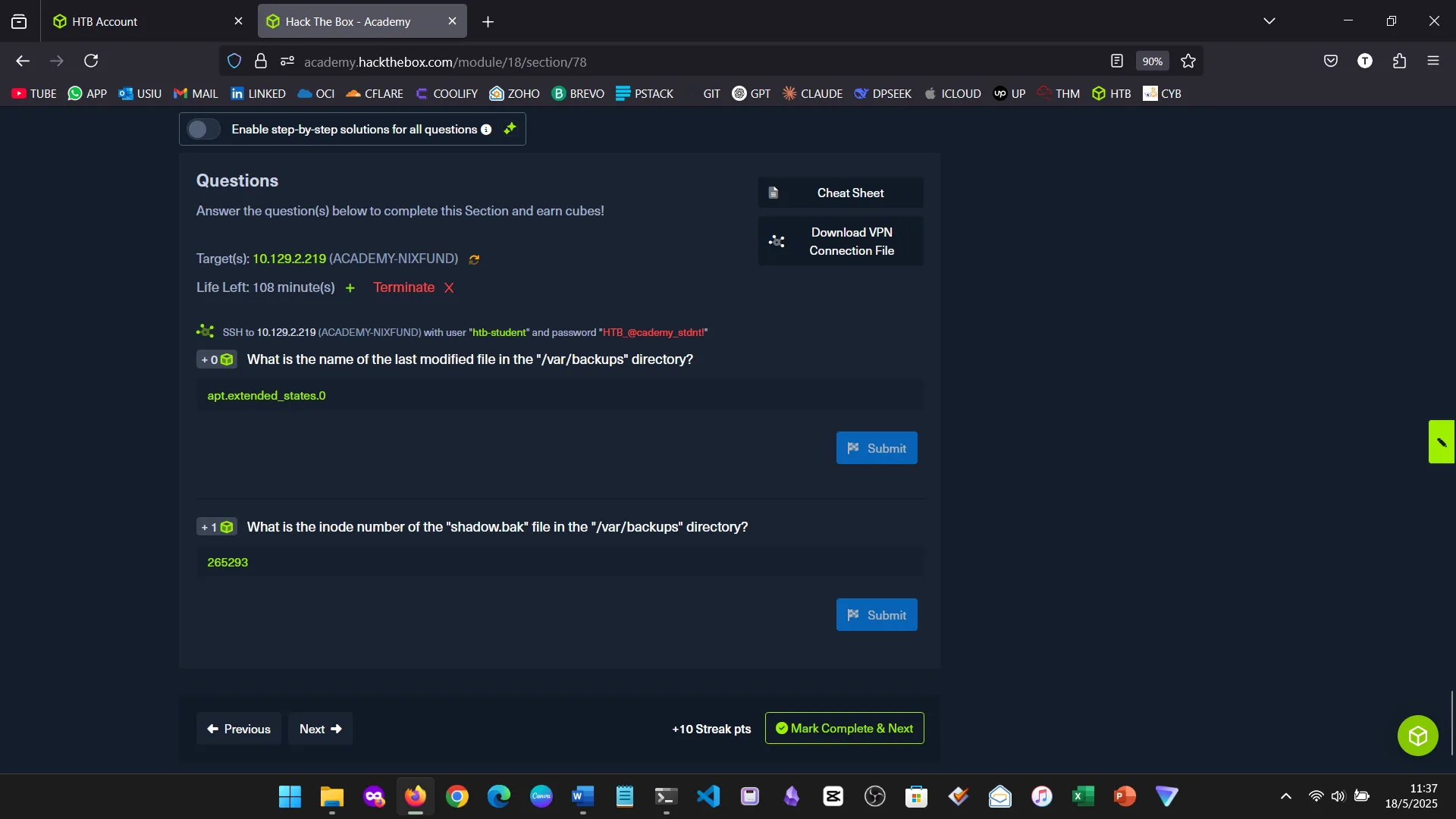
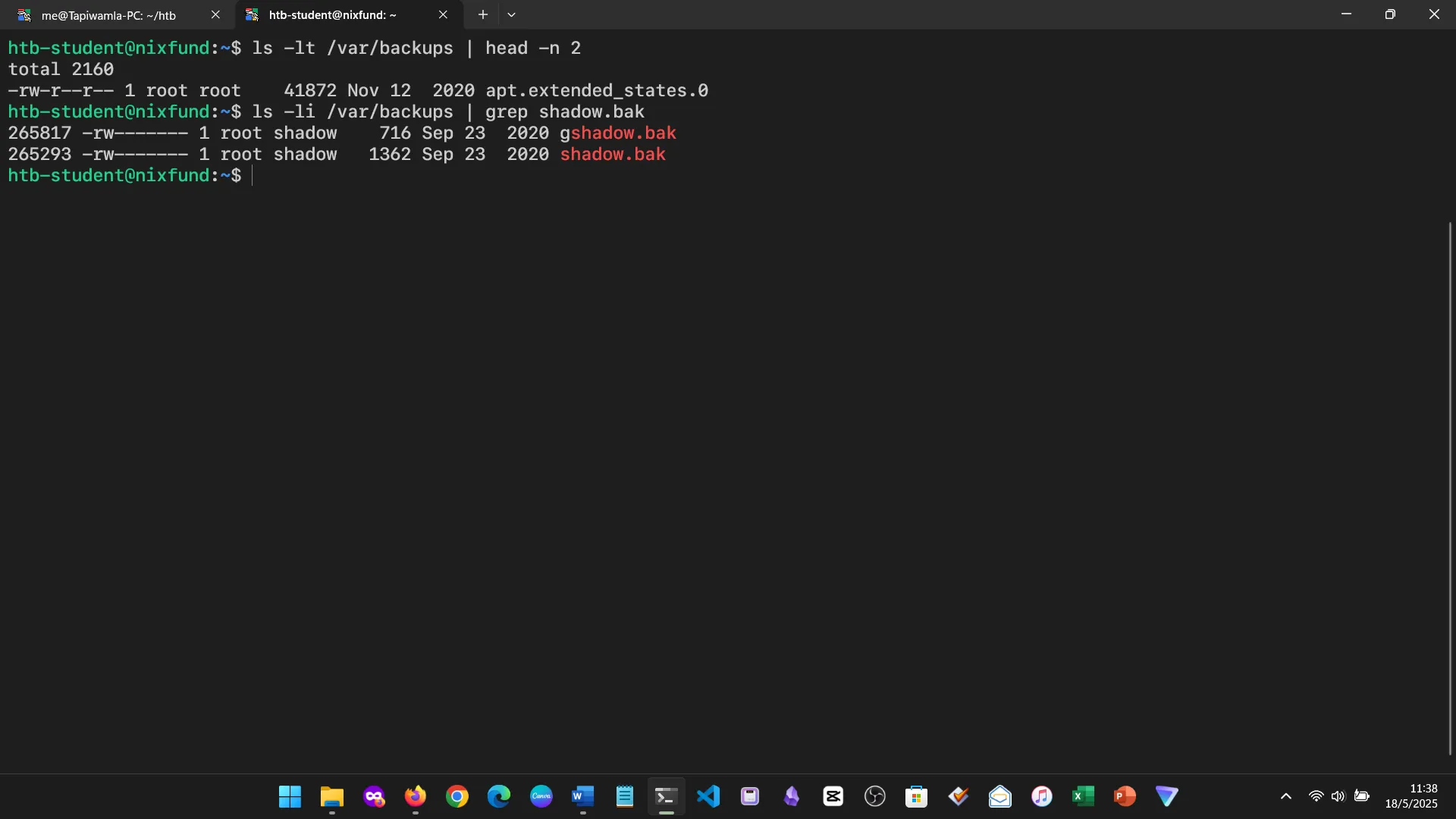
6. EDITING FILES & FINDING THEM
I explored Nano, Vi, and Vim. Vim remains my favorite for its speed and flexibility, especially with external program integration.
7. FILE DESCRIPTORS AND REDIRECTIONS
This section demystified STDIN, STDOUT, STDERR, redirection symbols, and pipes. Now I see how Linux manages I/O elegantly and how to chain commands effectively.
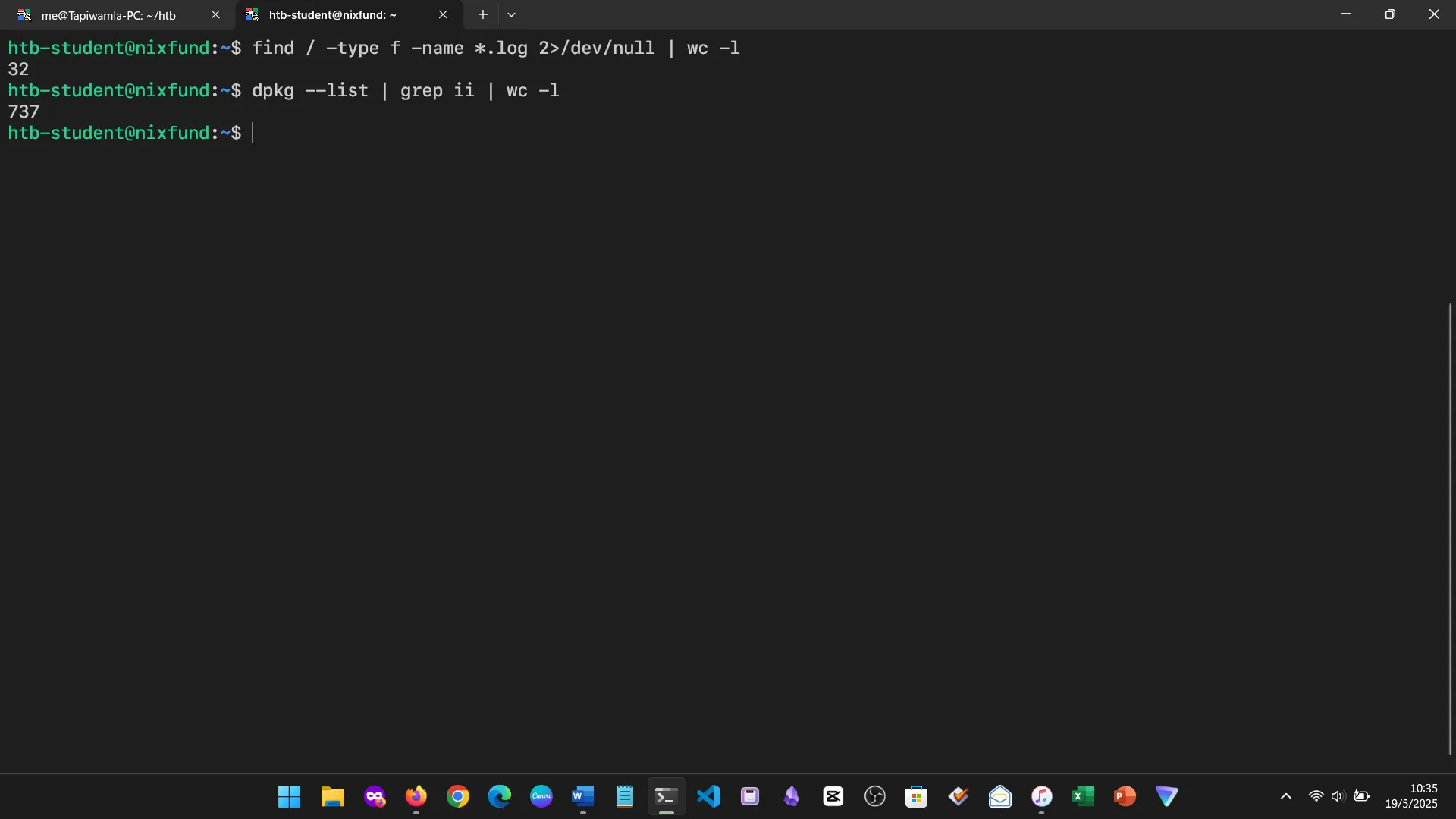
8. FILTER CONTENTS
Learned how to use tools like grep, awk, sed, cut, head, tail, tr, wc, etc. Very useful for automating text processing and analysis.
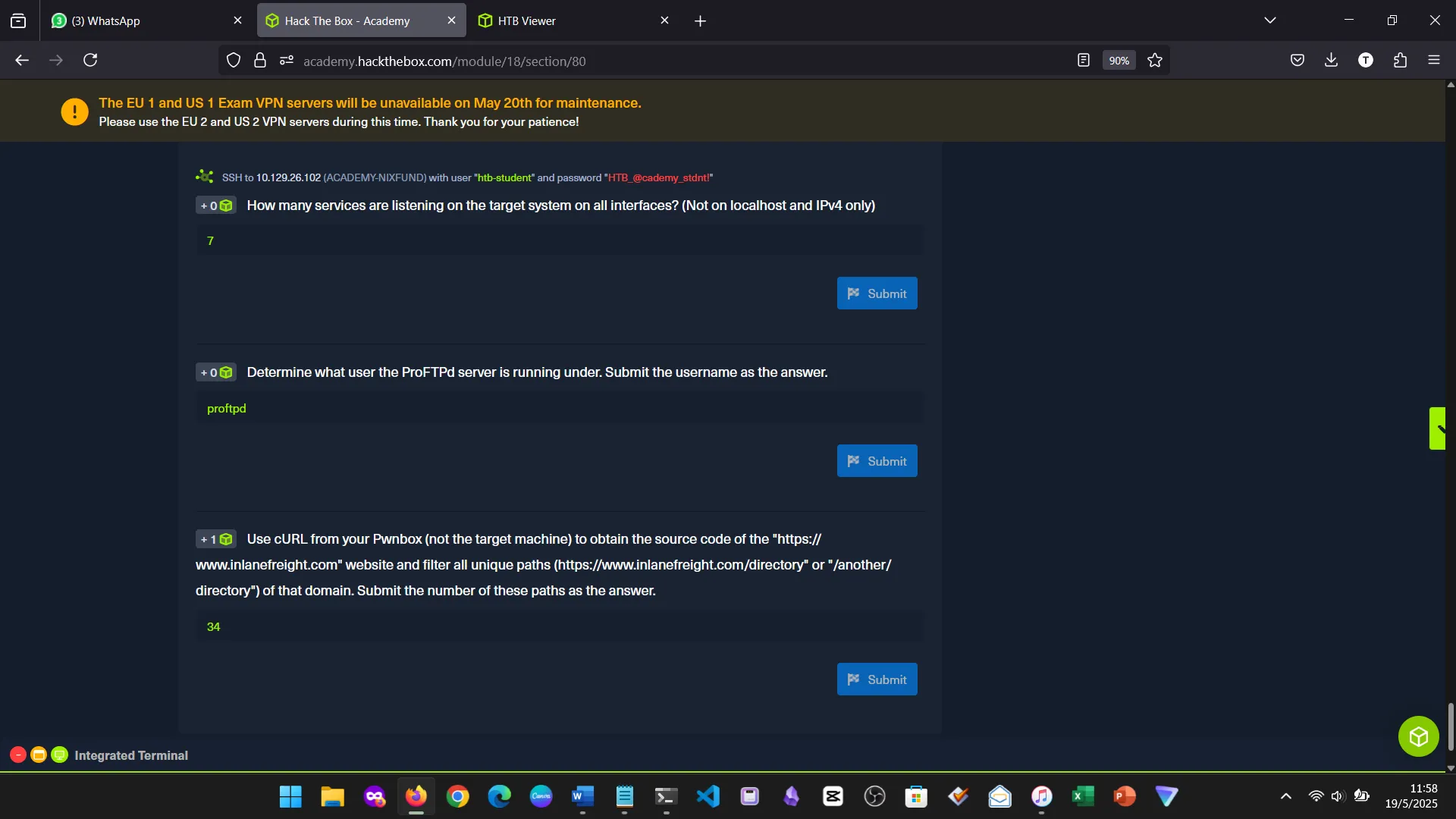
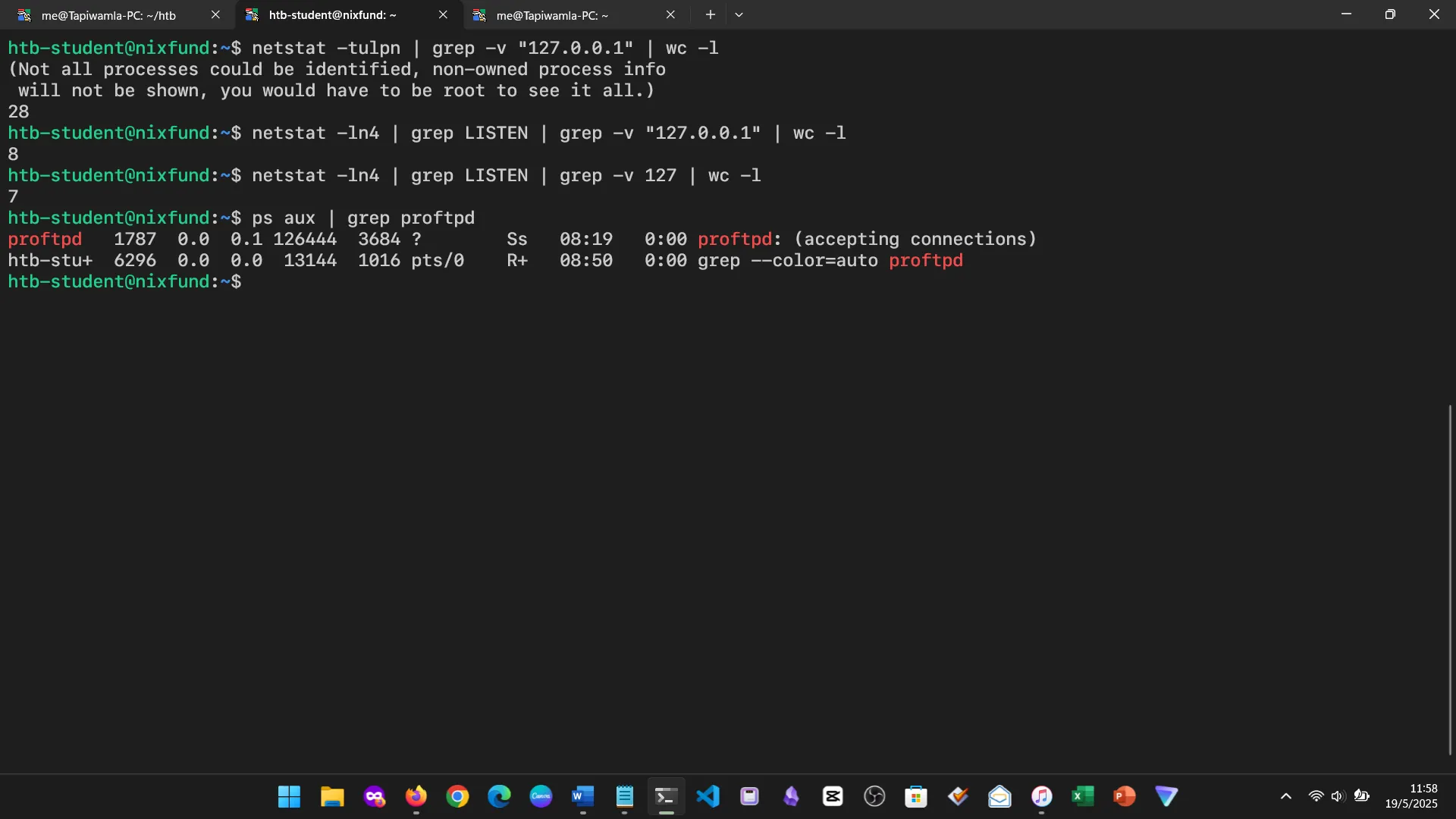
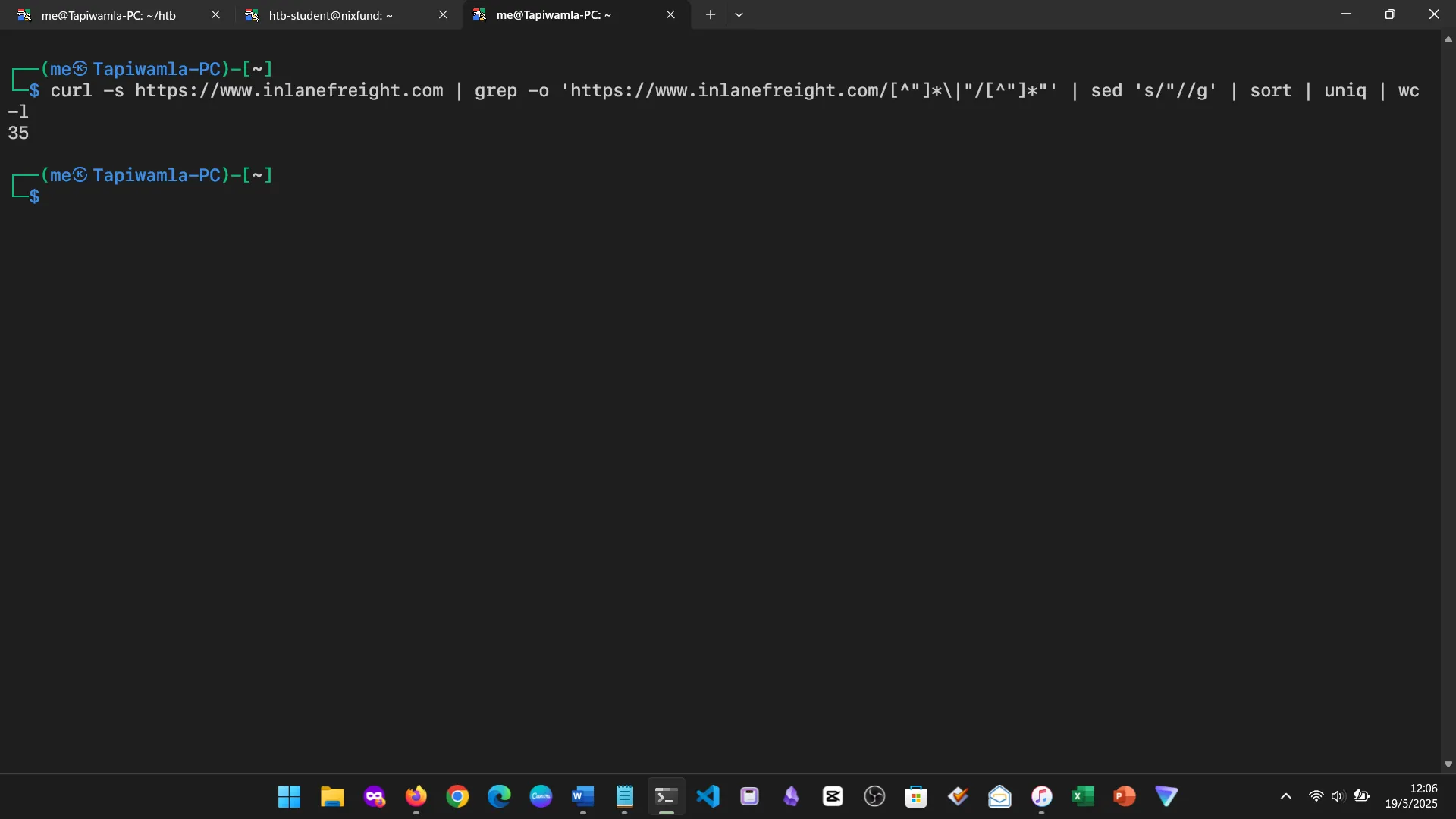
9. REGEX & PERMISSION MANAGEMENT
Regular Expressions were introduced for pattern searching. We also reviewed file permissions and how to manage them with chmod, chown, and related tools.
10. USER MANAGEMENT
Explored user account operations using useradd, usermod, passwd, and privilege escalation with sudo and su.
11. PACKAGE MANAGEMENT
Learned to install, update, and remove software using tools like apt, dpkg, pip, gem, snap, and git.
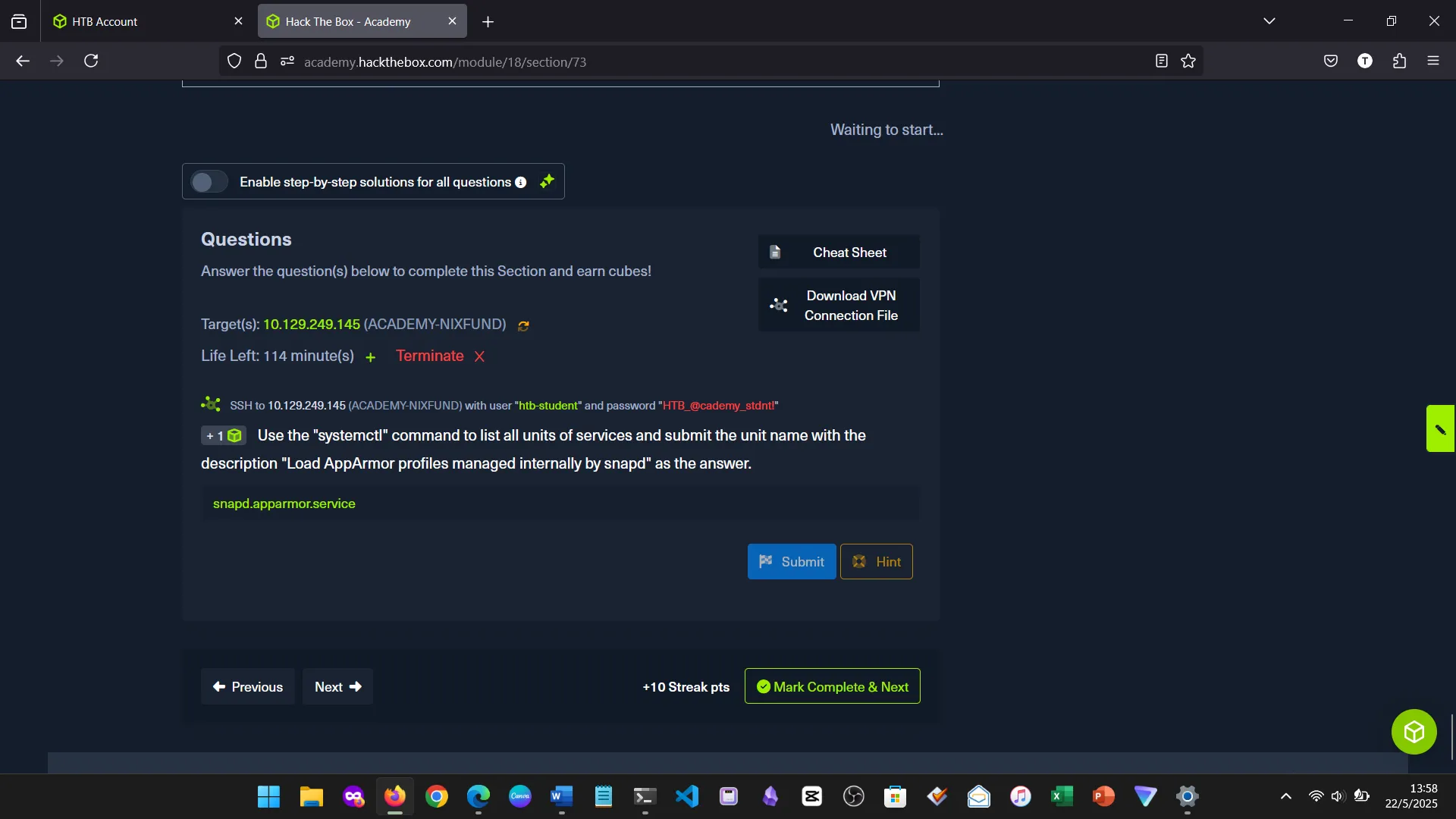
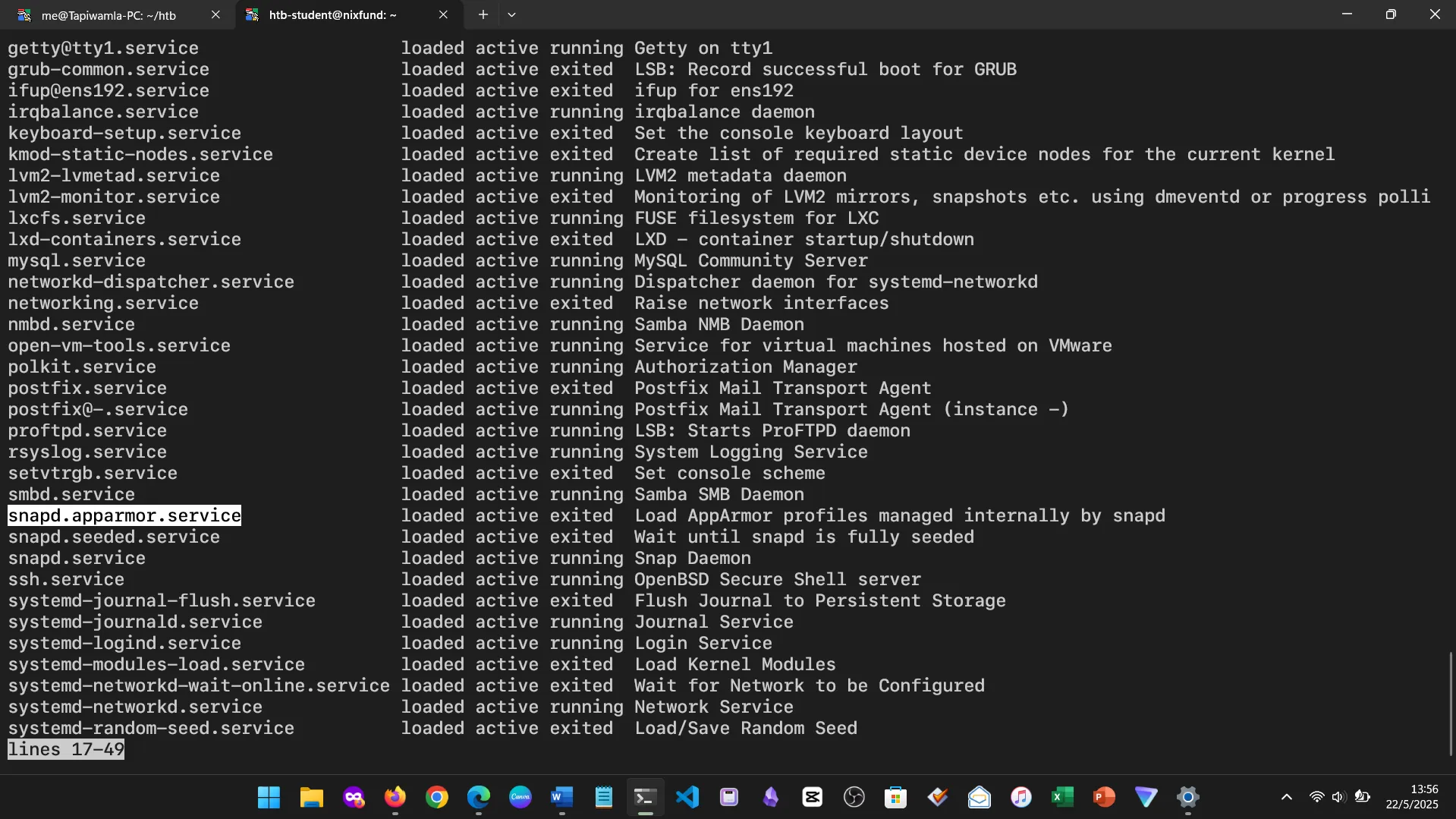
12. SERVICE AND PROCESS MANAGEMENT
Used systemctl, ps, kill, and journalctl to manage and inspect system services and background processes.
13. TASK SCHEDULING
Automated jobs with cron and systemd timers. These are essential for regular tasks like backups or updates.
14. NETWORK SERVICES
Reviewed SSH, NFS, and other core services that support communication, file transfer, and remote access.
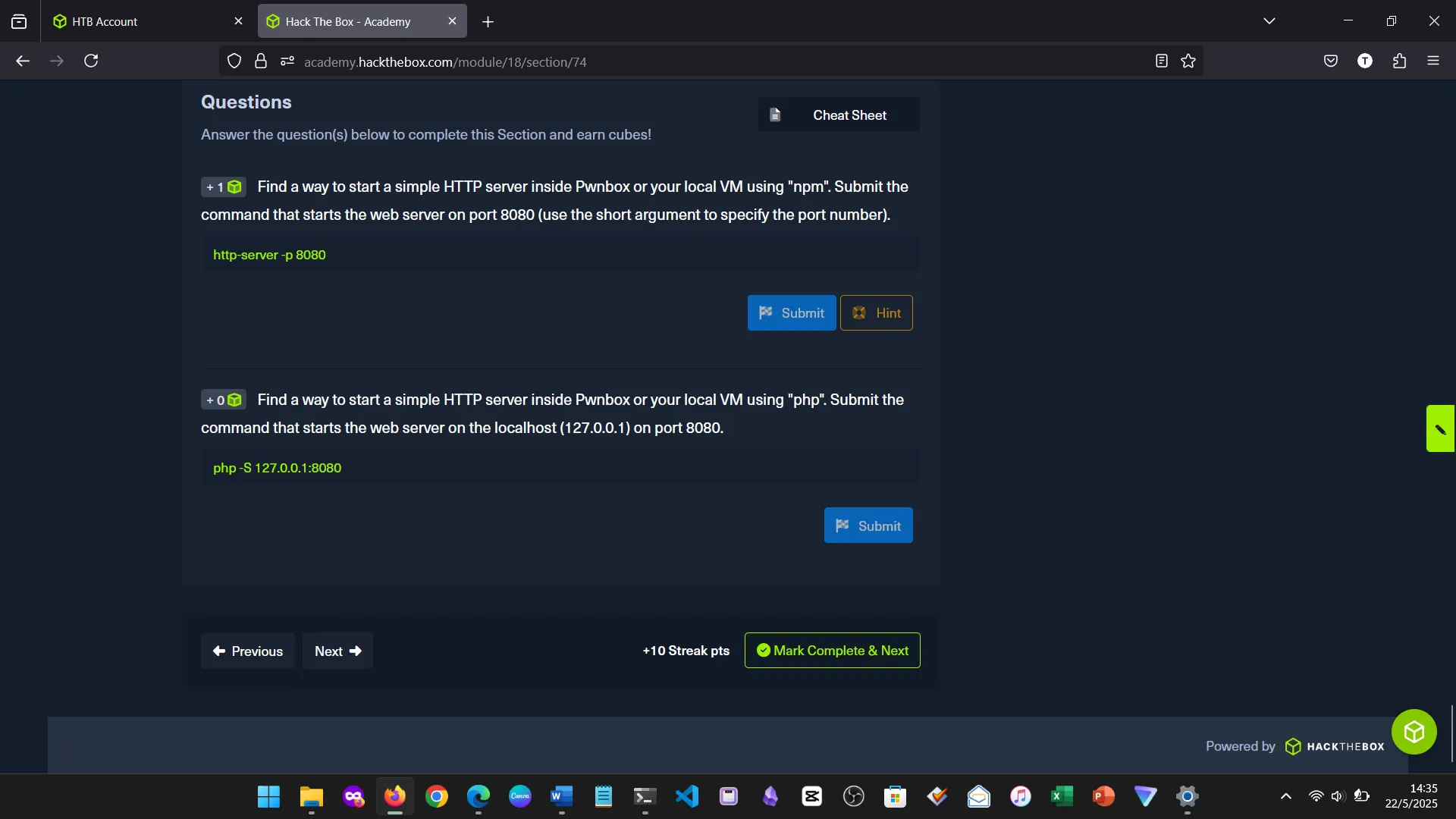
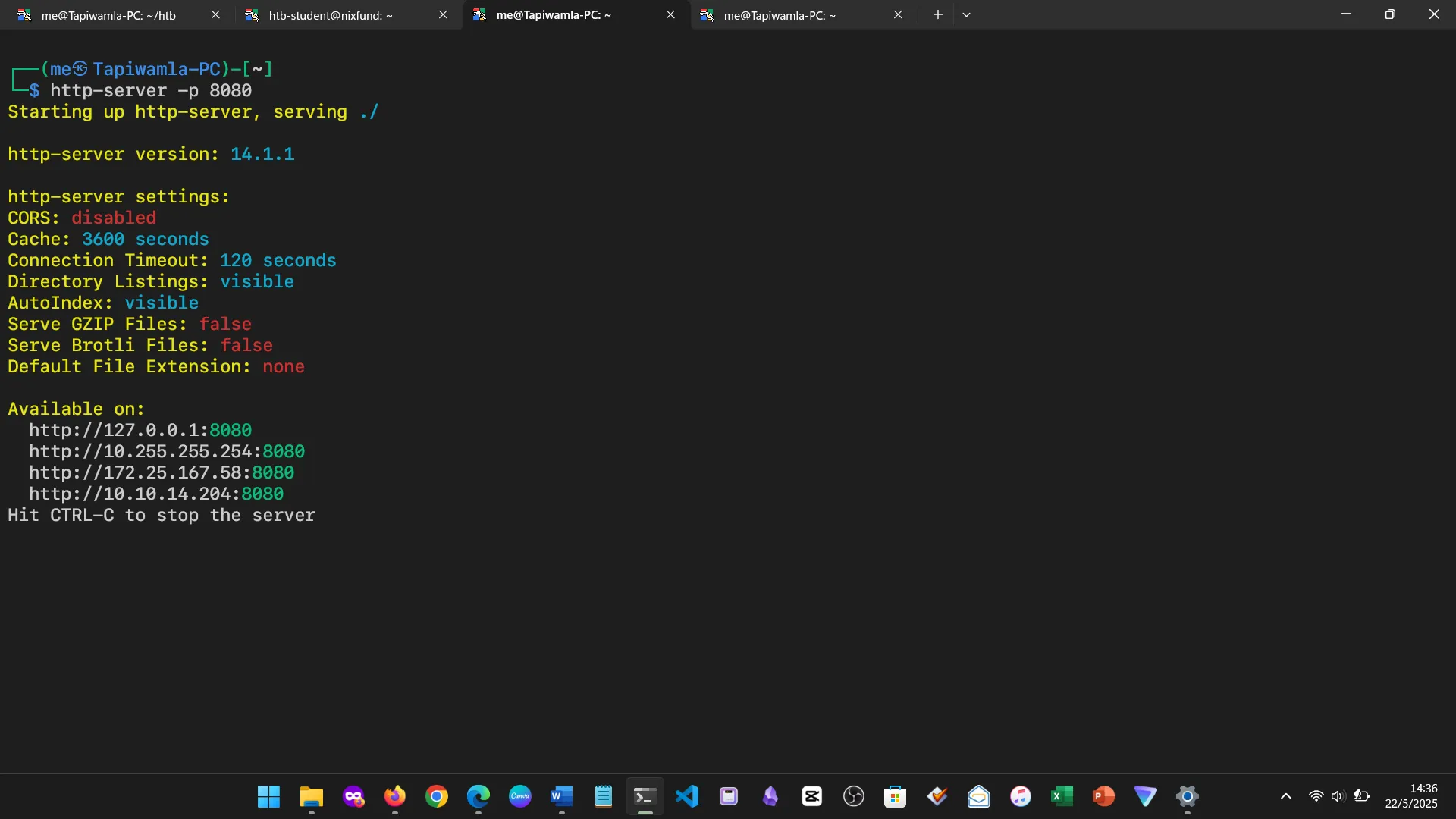
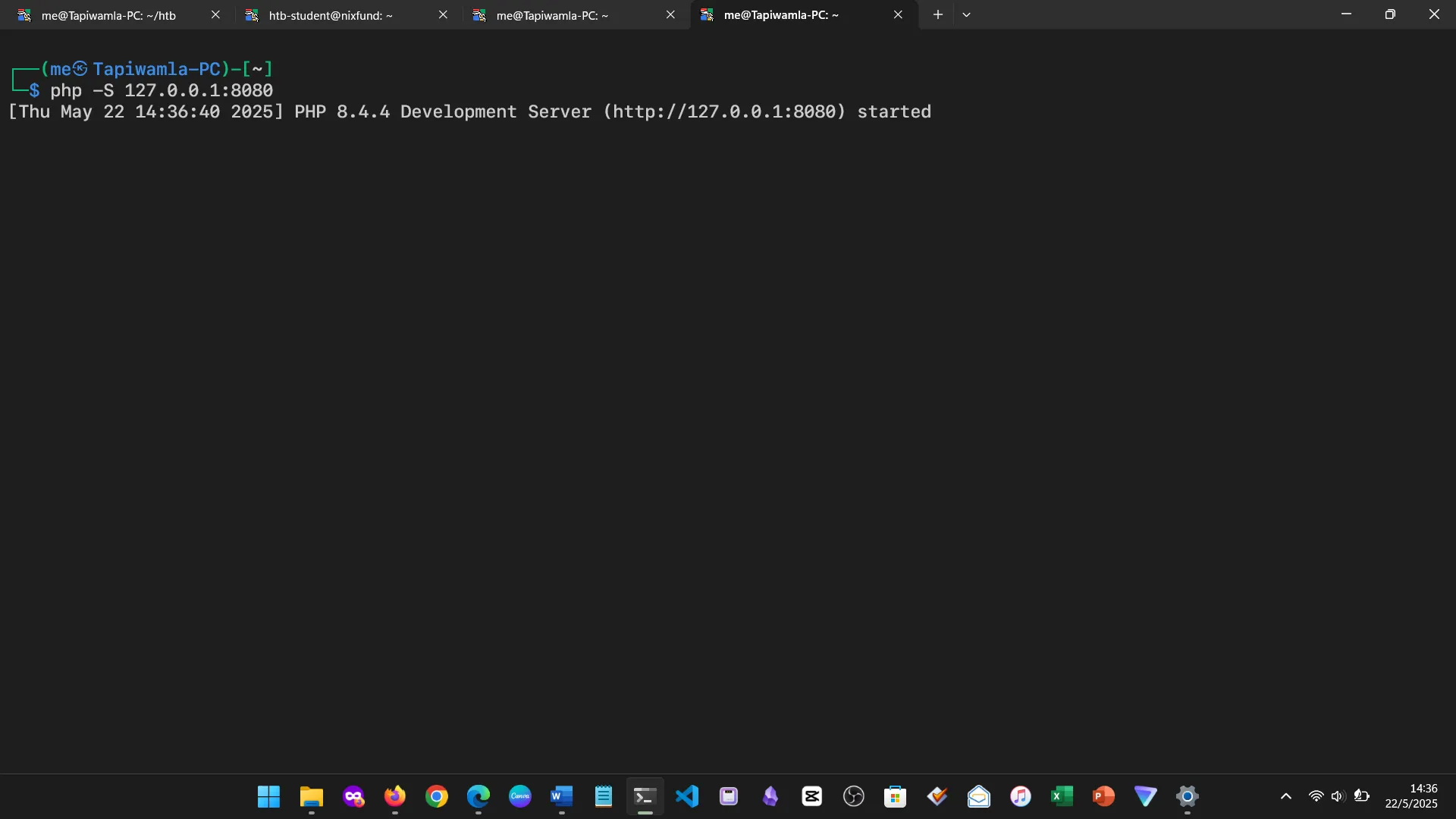
15. WEB SERVICES
Set up basic web servers using Apache, PHP, and Node. I interacted with them using curl and wget.
16. BACKUP AND RESTORE
Practiced using rsync to back up and restore data. Learned how encryption and automation strengthen backup routines.
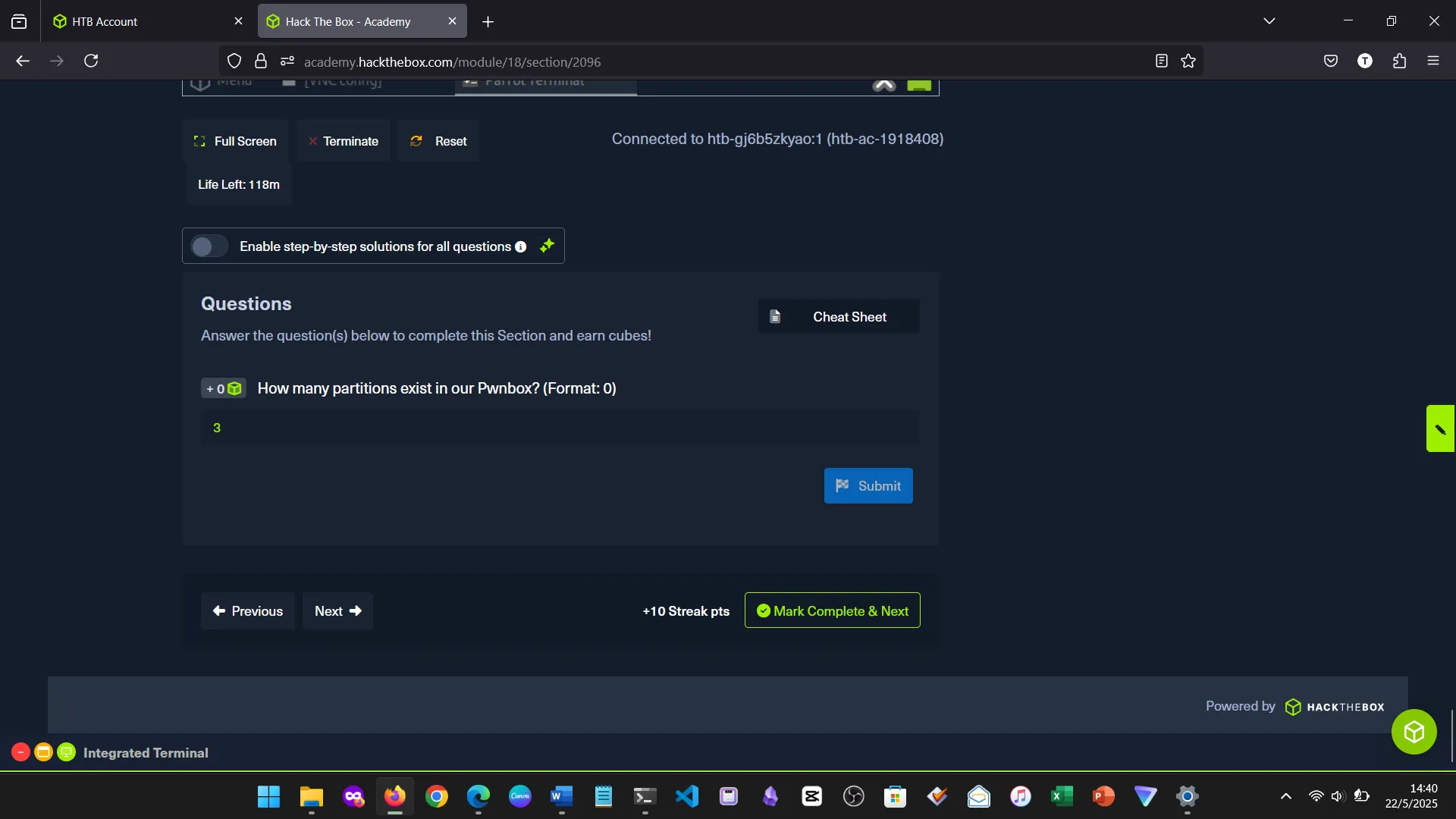
17. FILE SYSTEM MANAGEMENT
Explored different filesystems: ext4, XFS, Btrfs, NTFS. Learned how to manage partitions with fdisk and mount storage.
18. CONTAINERIZATION
Installed Docker, built containers, and understood the difference between VMs and containers. Learned how containerization enables portability and isolation.
19. NETWORK CONFIGURATION
Configured interfaces with ip, ifconfig, and route. Reviewed firewalls with SELinux and AppArmor.
20. REMOTE DESKTOP PROTOCOLS
Learned about RDP, VNC, and X11 for managing systems remotely.
21. LINUX SECURITY
Focused on hardening Linux: updates, SSH config, fail2ban, AppArmor, SELinux, and least privilege enforcement.
22. FIREWALL SETUP
Configured firewalls using iptables, nftables, ufw, and firewalld. Practiced setting custom rules.
23. SYSTEM LOGS
Used journalctl, grep, tail to read kernel, auth, and service logs. Logs are essential for incident response and auditing.
24. CONCLUSION
Looking back, this Linux module reshaped my perspective on system administration and security. What began as a review evolved into a deep, hands-on immersion across the OS landscape—from containers with Docker to setting up cron jobs, securing firewalls, filtering logs, and tweaking SELinux. I leave this module with real-world readiness, a sharper command line mindset, and an eagerness to dive deeper into orchestration, system security, and Linux-based dev environments.