Module: Intro to Log Analysis
1. INTRODUCTION
I have just completed the Intro to Log Analysis room on TryHackMe — a comprehensive, 1-hour introduction to log analysis, best practices, and essential tools for effective detection and response.
2. BASICS
Logs are recorded events or transactions within a system, device, or application. These include:
- Application Logs – Messages from applications about status, errors, and warnings.
- Audit Logs – Tracks actions and changes, offering user and system history.
- Security Logs – Security-related events like logins and permission changes.
- Server Logs – Includes system, event, error, and access logs.
- System Logs – Kernel and system events, boot sequences, hardware status.
- Network Logs – Captures data about connections and network activity.
- Database Logs – Tracks queries, updates, and actions in database systems.
- Web Server Logs – Records requests, IPs, request types, status codes, etc.
3. INVESTIGATION THEORY
Key investigation techniques include timeline construction to trace incidents, timestamp normalization, and building super timelines with tools like Plaso. Visualization tools like Splunk and Kibana help reveal patterns and anomalies.
Proactive detection includes SIEM alerting and use of threat intel (IPs, hashes, domains) to guide investigations.
4. DETECTION ENGINEERING
Covers common log locations (e.g., /var/log/nginx/access.log, /var/log/syslog) and patterns indicating attacks like failed logins, odd times, or suspicious user-agents (Hydra, Nmap). Recognizable patterns of SQLi, XSS, and LFI were explored.
5. AUTOMATED VS MANUAL ANALYSIS
- Automated Tools: XPLG, Loggly, etc. Efficient but expensive and can miss novel threats.
- Manual Analysis: Slower, but better context and control. Uses tools like
grep,awk,cut, etc.
6. LOG ANALYSIS TOOLS: COMMAND LINE
-
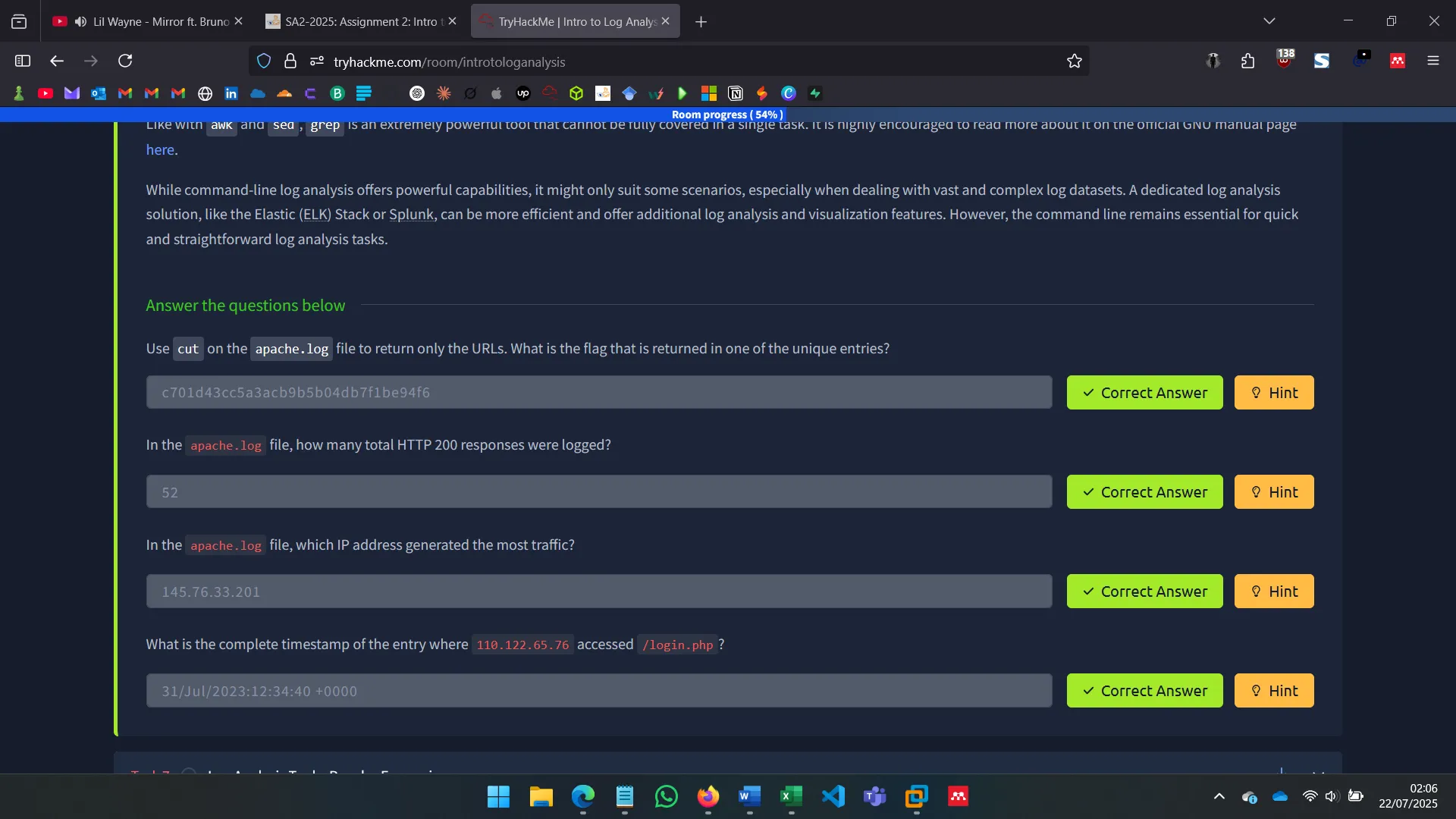
URLs extraction with cut
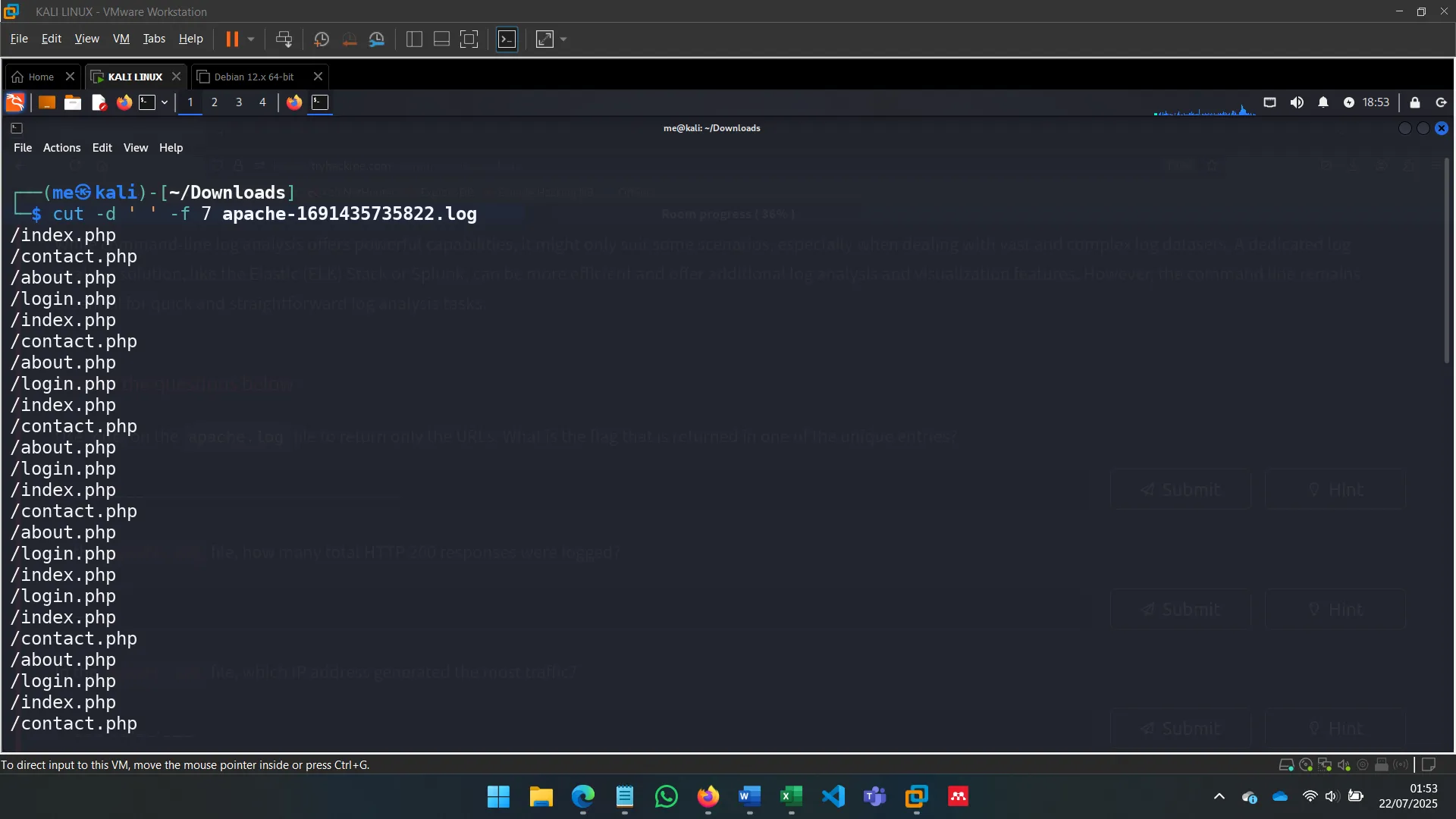
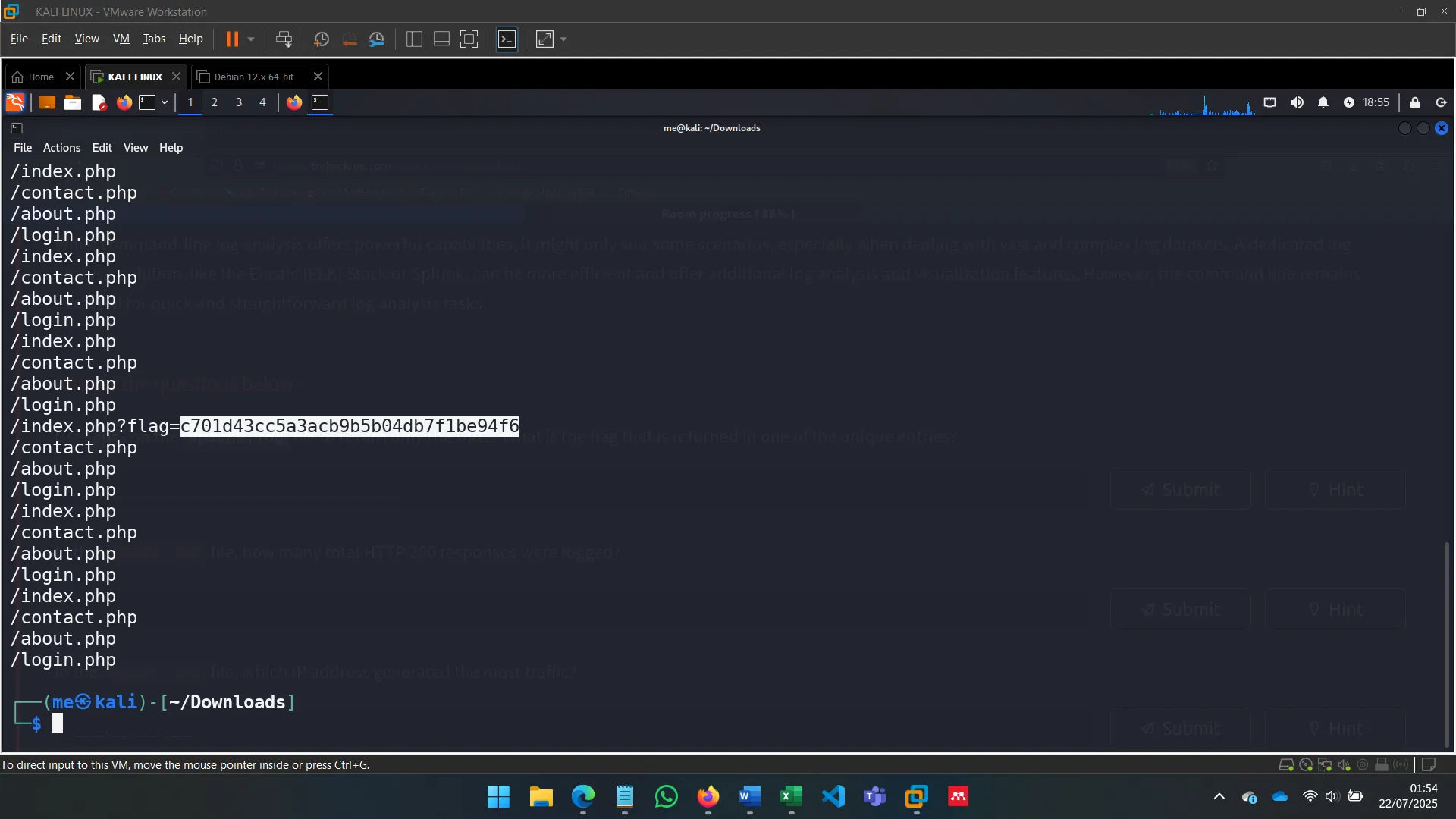
-
Count of HTTP 200 responses
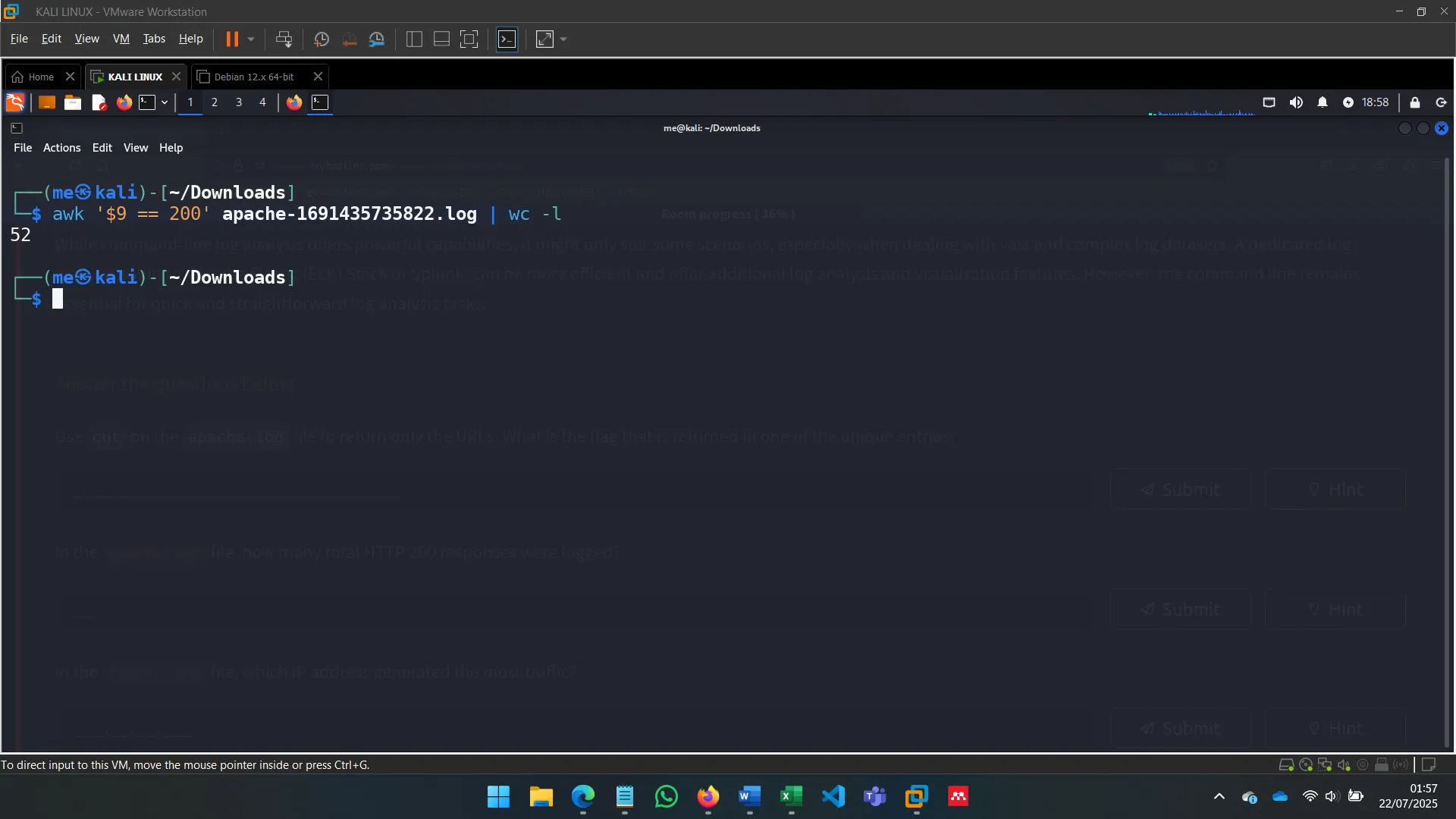
-
Top IP address by traffic
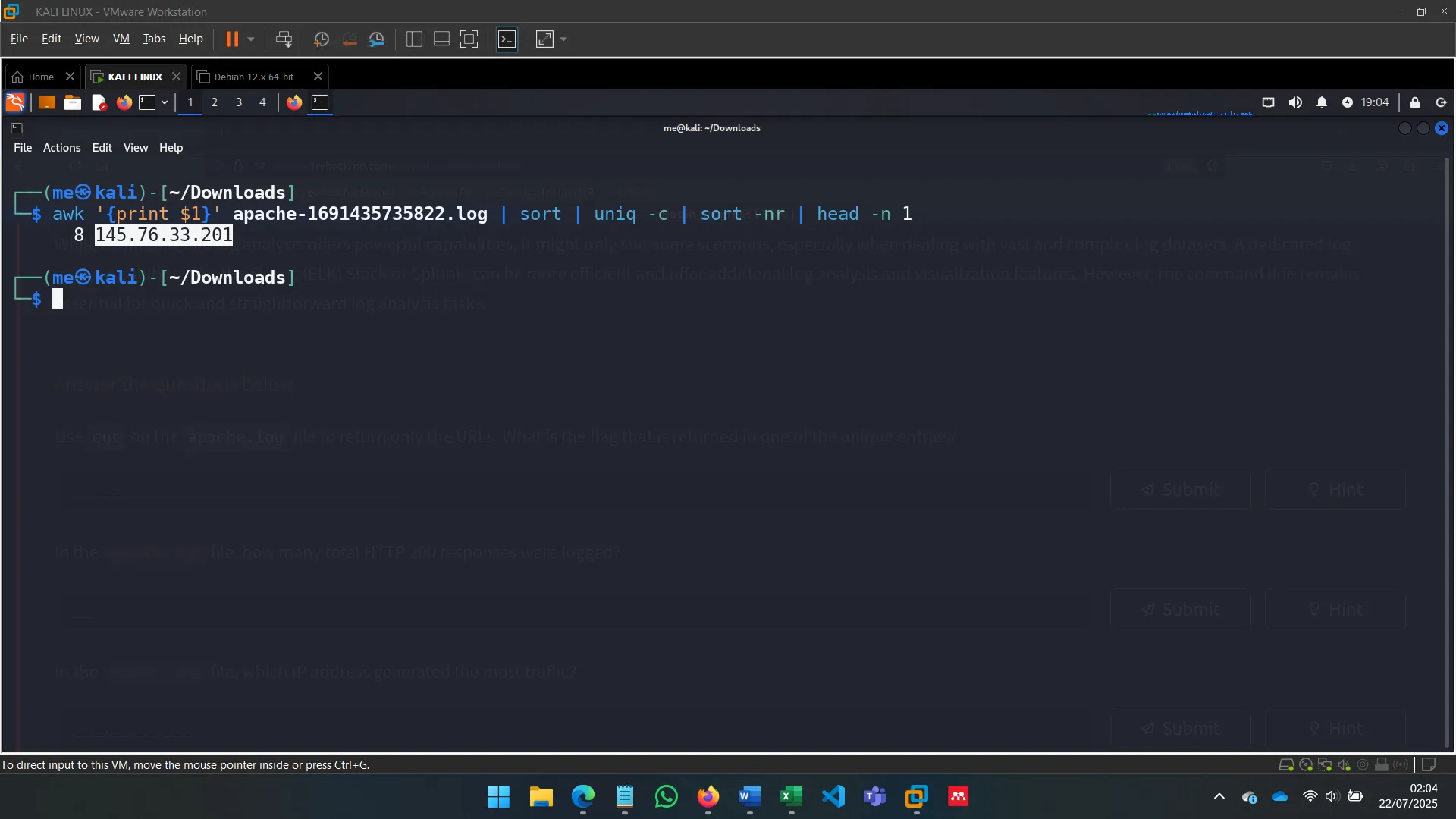
-
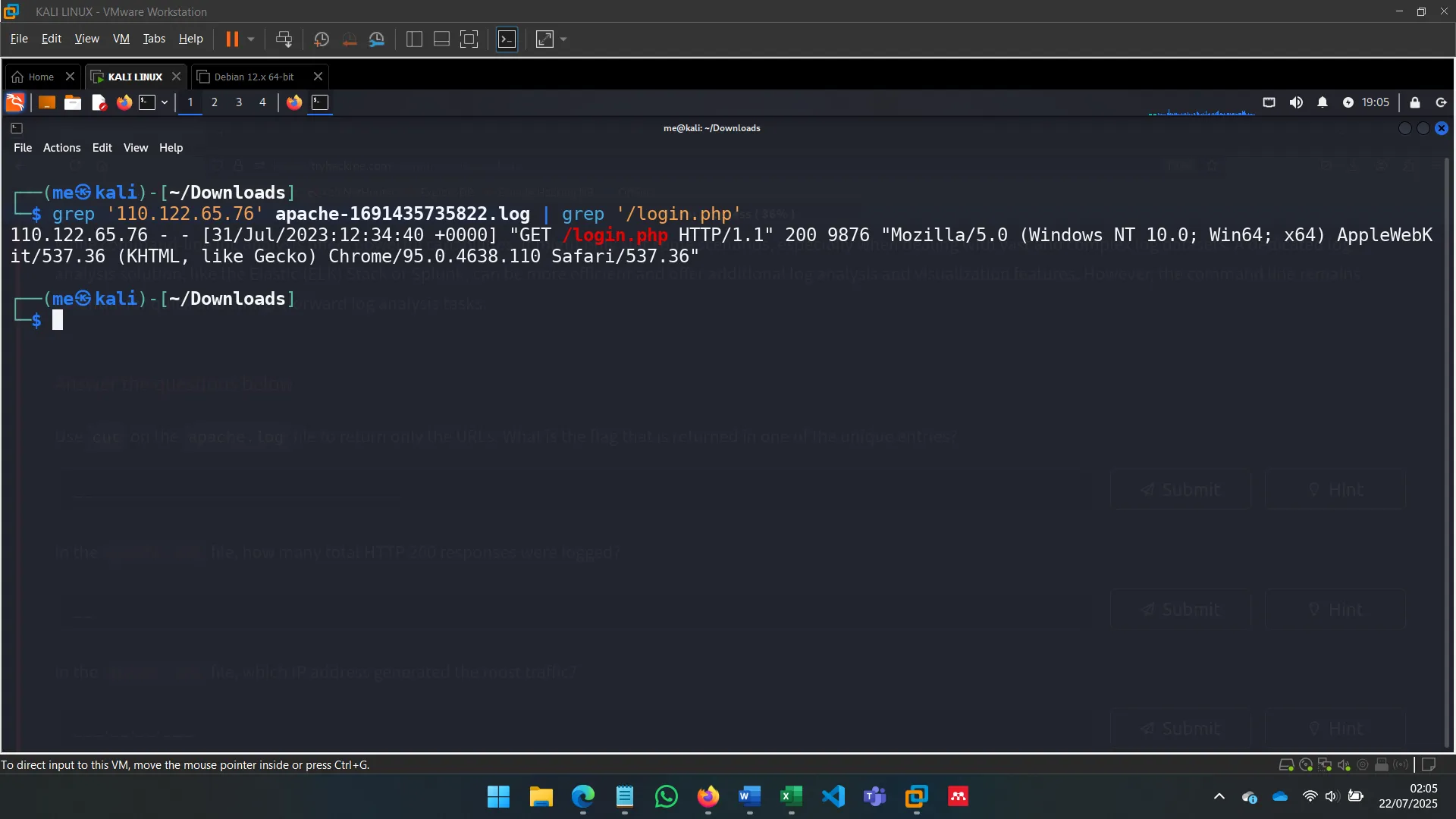
Timestamp for /login.php access by 110.122.65.76
7. LOG ANALYSIS: REGULAR EXPRESSIONS
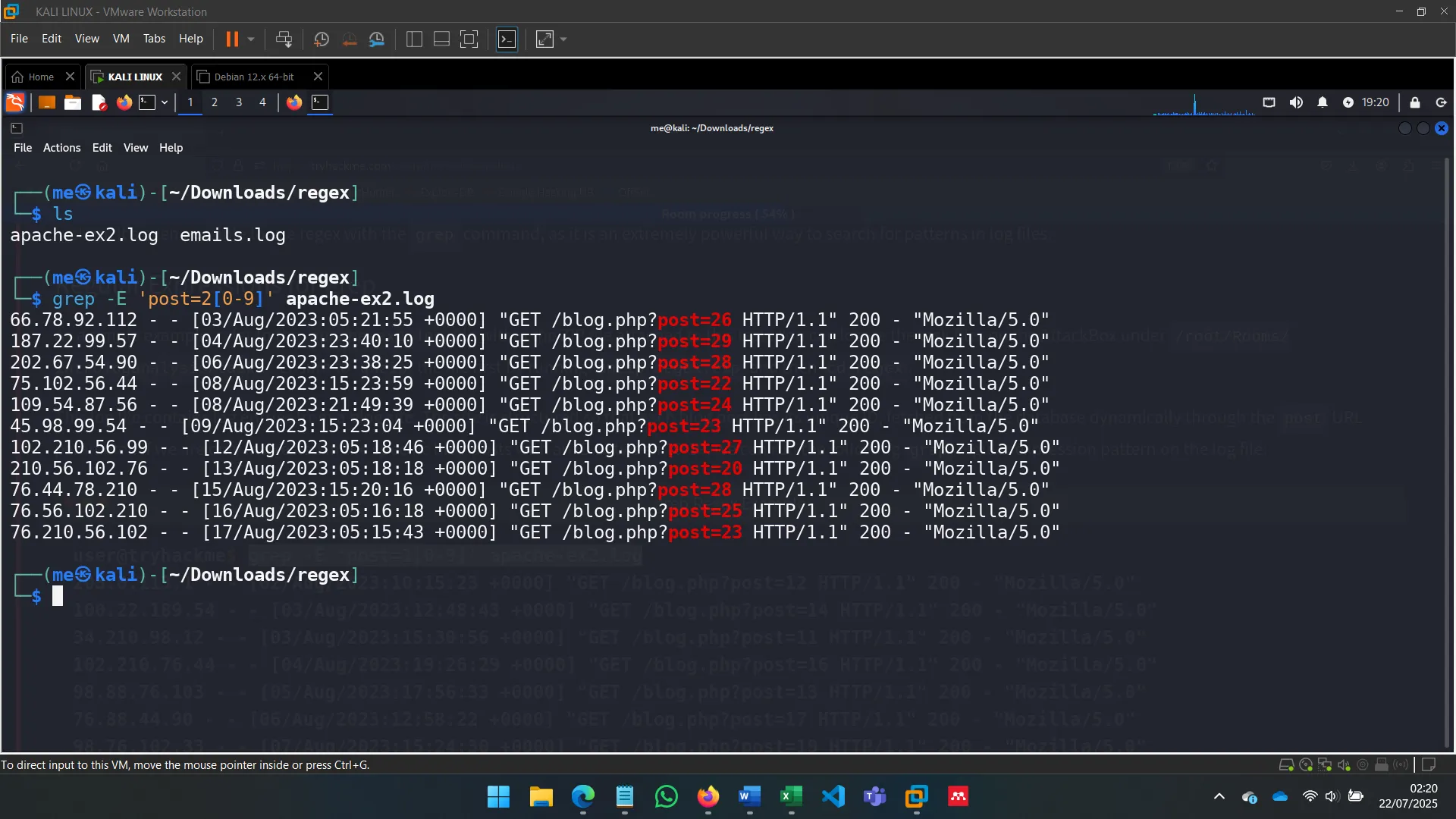
Regex is essential in extracting patterns from unstructured logs. For example, isolating blog posts with IDs 10–19 using grep.
Regex is crucial for parsing before ingestion into SIEMs. Tools:
- RegExr – pattern testing
- Grok – Logstash plugin to parse logs like
%{IP:client}
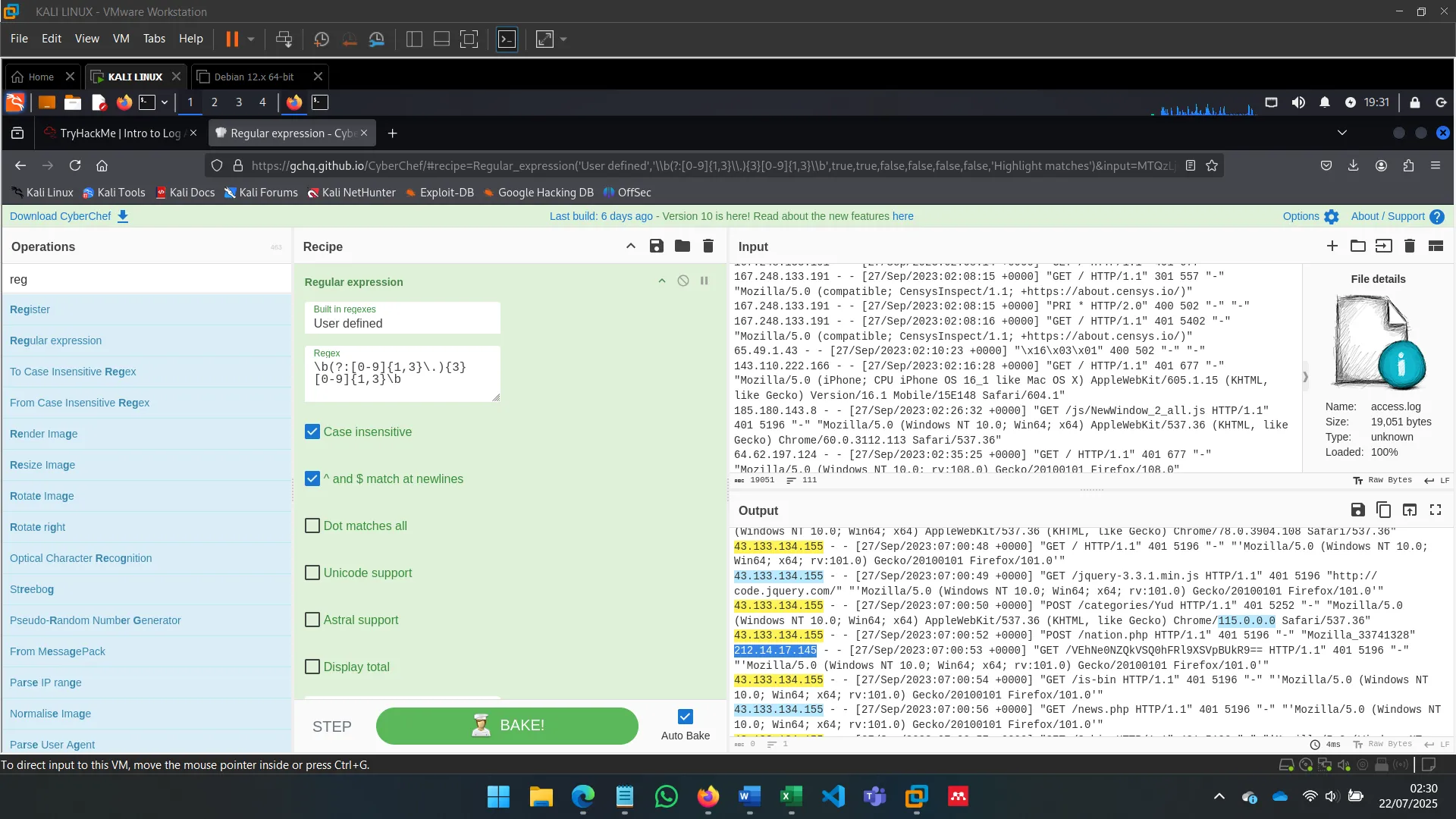
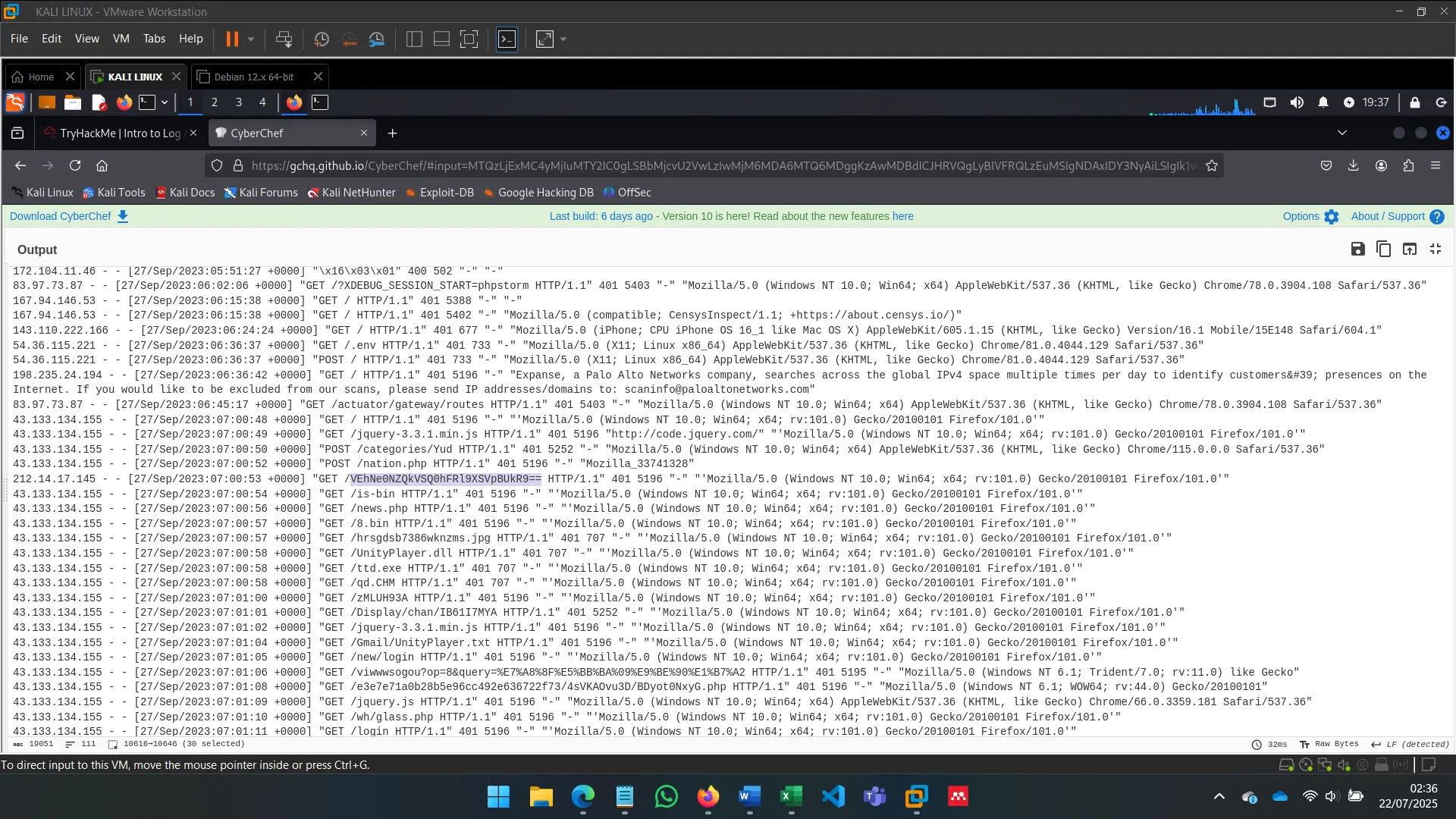
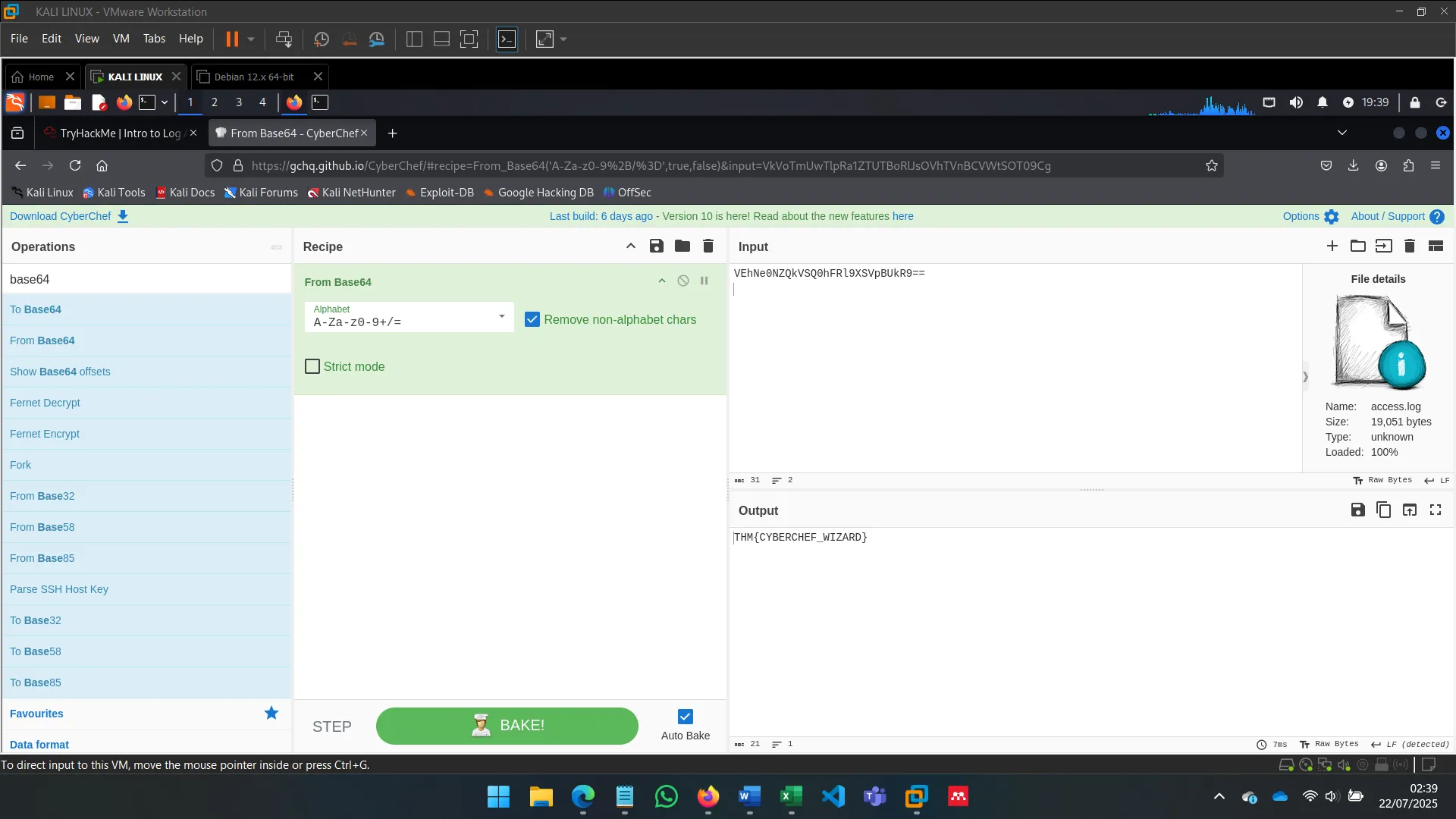
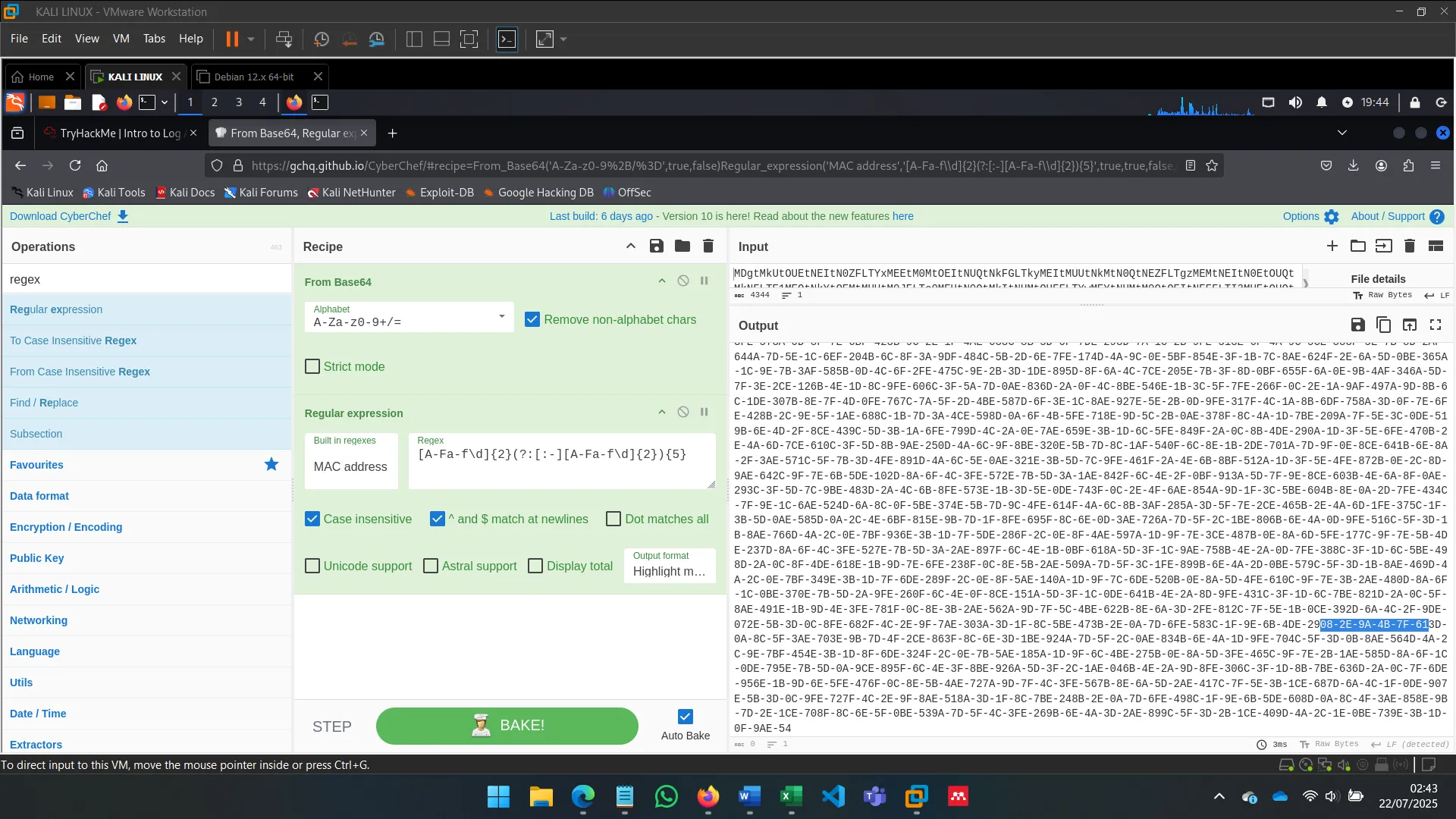
8. LOG ANALYSIS TOOLS: CYBERCHEF
CyberChef is a flexible data manipulation platform. Features:
- Encoding/decoding
- Encryption/hashing
- Log file parsing
- Data extraction
9. LOG ANALYSIS: YARA AND SIGMA
- Sigma: YAML rules for log detection in SIEMs (e.g., failed SSH logins).
- Yara: Pattern matching in binary/text for malware detection or IP matches.
Essential tools for threat hunting and detection.
10. CONCLUSION
This room was a solid introduction to log analysis and the tools that support it. It was also a great refresher on command-line utilities like grep, awk, sed, and wc. Regex was also fun to tinker with again. A useful module overall.